Population Dynamics of Bald Eagles in the Northeast US
We integrate information from veterinary science and ecology to discover interesting and exciting facts where mathematics, computer science, resource management, and ornithology converge.
We used novel techniques to assess the population-scale impacts of Pb toxicosis in bald eagles in the northeastern US.
Life history of bald eagles
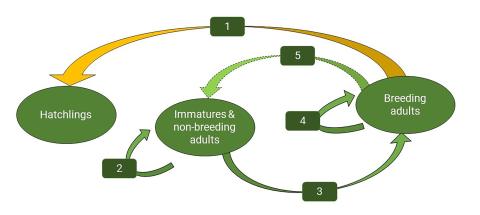
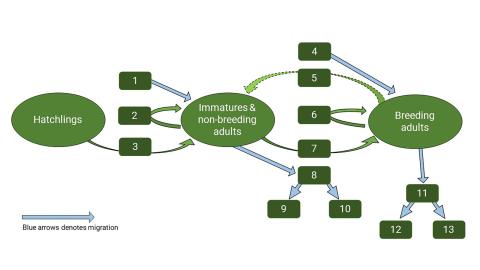
Life cycle graphs accurately reflect the biology of wildlife and are the mathematical building blocks of their projection matrix (de Kroon et al. 2000). We used a 3-stage matrix (Lefkovitch 1965) that contains bi-annual periods (Gallardo et al. 2019), density dependence (Caswell 2001), and stage-structured migration parameters. The matrices for the breeding and non-breeding periods are folded into a single annual model matrix (Hanley et al. 2019).
Key:
- Fecundity of breeding bald eagles.
- Failure of an immature or non-breeding bald eagle to move up into the breeding category.
- Successful transition of an immature or non-breeding bald eagle into the breeding category.
- Survival of an iteroparous adult bald eagle.
- The demotion of a breeding bald eagle into the non-breeding category.
Key:
- (Before fall) Seasonal immigration of non-resident immatures or non-breeders.
- Failure of an immature or non-breeding bald eagle to move up into the breeding category.
- Successful fledging of a hatchling into the immature category.
- (Before fall) Seasonal immigration of non-resident breeders.
- The demotion of a breeding bald eagle into the non-breeding category.
- Survival of an iteroparous adult bald eagle.
- Successful transition from an immature or non-breeding adult into a breeding adult.
- (Before fall) Seasonal emigration of part-time resident immatures or non-breeders into an alternative geographical system.
- (After fall) Dispersion of resident immatures or non-breeders into an alternative geographical system.
- (After fall) Return immigration of part-time resident immatures or non-breeders.
- (Before fall) Seasonal emigration of part-time resident breeders into an alternative geographical system.
- (After fall) Dispersion of resident breeders into an alternative geographical system.
(After fall) Return immigration of part-time resident breeders
Population scale impact of lead (Pb) toxicosis on eagles
The population scale impact of lead (Pb) toxicosis in eagles is an important topic in wildlife management. We developed the CounterPOPd software to compare current (factual) and hypothetical (counter factual) population dynamics of bald eagles in the northeast US under Pb, Pb-reduced, and Pb-free conditions. Please see the published results in Hanley et al. (2022).
Additional questions
What are the current population dynamics of eagles in the northeast US?
Please see the published results in Hanley et al. (2019) or at doi.org/10.7298/q4m1-se95.
If the northeast US had been closed to dispersal, how would Pb have affected their recovery?
Please see doi.org/10.7298/q4t7-1y54.
Can I conduct my own sensitivity analysis? Sure!
Please see published results in Hanley, Connelly, and Dennis (2019) or at doi.org/10.7298/bcmg-7w08.
What are the impacts at hypothetically higher or lower densities?
Please see doi.org/10.7298/6yb8-5c25.
How has Pb influenced this plasticity in eagles?
Please see doi.org/10.7298/7rxf-ee77.
Using novel computational technologies, we can assess the population-scale impacts of a disease, toxin, or contaminant on bald eagles.
Presentation at the 2020 Annual Conference for the Ecological Society of America
Ask for additional information
Questions can be directed to Dr. Krysten Schuler.
Financial support was provided in part by the Morris Animal Foundation under grant # D18ZO-103, in part by the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation, and in part by the Federal Aid in Wildlife Restoration Grant W-178-R Wildlife Health. The contents of this website, links, interactive apps, cited literature, and narratives have not been reviewed nor endorsed by the Foundation or Department, and the views expressed in this content do not necessarily reflect the views of the Foundation or the Department, its officers, directors, affiliates or agents.
- Bald eagle rebound stunted by poisoning from lead ammunition by Krishna Ramanujan in the Cornell Chronicle, 13 January 2022.
- Lead diminished bald eagle recovery and continues to pose risks by David Frey at The Wildlife Society, 13 January 2022.
- Eagles still feel weight of lead in environment at the Morris Animal Foundation, 13 January 2022.
- Lead ammo poisoning threatening bald eagle population, study says by Joseph Guzman at The Hill, 13 January 2022.
- Lead ammo hampers the bald eagle rebound in the Northeast US by Brian Bienkowski at Environmental Health News, 14 January 2022.
- Bald eagle population growth stunted by lead poisoning, study finds by Alexandra Larkin at CBS News, 14 January 2022.
- The bald eagle population slowly recovers, but lead ammo hampers their resilience by Rina Torchinsky at NPR, 14 January 2022.
- U.S. bald eagles comeback diminished by lead poisoning from bullets by Barbara Goldberg at Reuters, 14 January 2022.
- Bald eagle comeback impacted by lead poison by Sharon Udasin and Saul Elbein at The Hill, 14 January 2022.
- Bald eagles are being poisoned by lead ammo in hunted animals. Could copper bullets be the fix? by Rita Giordano at The Philadelphia Inquirer, 3 February 2022.
- Lead Bullets Are Stunting the Bald Eagle's Recovery by Spoorthy Raman at Audubon, 3 February 2022.
- Lead poisoning is suppressing eagle populations by David Frey at The Wildlife Society, 17 February 2022.
- Nearly half of US bald eagles suffer lead poisoning by Christina Larson at the AP, 17 February 2022.
- Nearly half of bald eagles have lead poisoning by Tess Joosse at Science, 17 February 2022.
- Bald Eagle Population Growth Rate Suppressed by Lead Poisoning by Aylin Woodward at the Wall Street Journal, 17 February 2022.
This research contains diverse and interdisciplinary contributions from professionals all over the region. Contributions may include intellectual property, knowledge, data, software code, time, ideas, suggestions, comments, reviews, a professional network, and communication materials.
We thank (alphabetical order):
Alyssa Kaganer, Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell Wildlife Health Lab, Ithaca, New York, USA
Amy McMurtry, Graphical Artist, Moscow, Idaho, USA
André A. Dhondt, Lab of Ornithology, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, USA
Barb Bodenstein, United States Geological Survey, National Wildlife Health Center, Madison, Wisconsin, USA
Brenda Hanley, Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell Wildlife Health Lab, Ithaca, New York, USA
Brian Hess, Connecticut Department of Energy and Environmental Protection, Hartford, Connecticut, USA
Cara Them, Corvallis, Oregon, USA
Chris Martin, New Hampshire Audubon, Concord, New Hampshire, USA
David Needle, New Hampshire Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory, University of New Hampshire, Durham, New Hampshire, USA
David O. Brown, Ithaca, New York, USA
David W. Kramer, New York Department of Environmental Conservation, Albany, New York, USA
Diane Winn, Avian Haven Wild Bird Rehabilitation Center, Freedom, Maine, USA
Dieter Heylen, Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey, USA, Interuniversity Institute for Biostatistics and statistical Bioinformatics, Hasselt University, Diepenbeek, Belgium
Elizabeth M. Bunting, Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell Wildlife Health Lab, Ithaca, New York, USA
Ernesto Dominguez-Villegas, Independent Wildlife Consultant, Virginia, USA
Florina Tseng, Wildlife Clinic & Center for Conservation Medicine, Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine Tufts University, North Grafton, Massachusetts, USA
Jennifer Peaslee, Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell Wildlife Health Lab, Ithaca, New York, USA
Justin D. Brown, Department of Veterinary and Biomedical Sciences, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pennsylvania, USA
Karyn L. Bischoff, Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine, Animal Health Diagnostic Center, Ithaca, New York, USA
Katherine McComas, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, USA
Kevin P. Hynes, New York Department of Environmental Conservation, New York, USA
Krysten L. Schuler, Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell Wildlife Health Lab, Ithaca, New York, USA
María J. Forzán, Cornell Wildlife Health Lab, Animal Health Diagnostic Center, Ithaca, New York, USA, and Department of Veterinary Biomedical Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, Long Island University, Brookville, New York, USA
Mark A. Pokras, Wildlife Clinic & Center for Conservation Medicine, Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine Tufts University, North Grafton, Massachusetts, USA
Mark Ruder, University of Georgia, Athens, Georgia, USA
Mary Garrison, Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell Wildlife Health Lab, Ithaca, New York, USA
Nick Hollingshead, Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell Wildlife Health Lab, Ithaca, New York, USA
Nicole I. Keith, Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell Wildlife Health Lab, Ithaca, New York, USA
Pamela Mills, Department of Lands and Forestry, Wildlife Division, Government of Nova Scotia, Nova Scotia, CA
Patrick Connelly, Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell Wildlife Health Lab, Ithaca, New York, USA
Patrick P. Martin, New York State Department of Environmental Conservation (retired), Middleburgh, New York, USA
Rachel Abbott, Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell Wildlife Health Lab, Ithaca, New York, USA
Samantha Gibbs, Wildlife Health Office, National Wildlife Refuge System, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Chiefland, Florida, USA
Sandra Houghton, New Hampshire Fish and Game Department, Concord, New Hampshire, USA
Sarah Ireley, Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell Wildlife Health Lab, Ithaca, New York, USA
Tom French, Division of Fisheries and Wildlife, Westborough, Massachusetts, USA
Wendy Kozlowski, John M. Olin Library, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, USA
And 17 additional anonymous professionals or academic reviewers.
Peer-reviewed research:
Hanley, B, Dhondt, A, Forzán, M, Bunting, E, Pokras, M, Hynes, K, Domínguez-Villegas, E, & Schuler, K. 2022. Environmental lead reduces the resilience of Bald Eagle populations. Journal of Wildlife Management. https://wildlife.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jwmg.22177
Hanley, B, Dhondt, A, Dennis, B, & Schuler, K. 2019. Using time series data to assess recent population dynamics of Bald Eagles in the northeast United States. Ecosphere. doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.2963
Hanley, B, Connelly, P, & Dennis, B. 2019. Another look at the eigenvalues of a population matrix model. PeerJ 7:e8018. doi.org/10.7717/peerj.8018
Hanley, B, Dhondt, A, Forzán, M, Bunting, E, Pokras, M, Hynes, K, Domínguez-Villegas, E, & Schuler, K. Bald Eagle Dashboard: Software to assess the population scale impact of anthropogenic mortality. In peer review.
Hanley, B, Connelly, P, Bunting, E, & Schuler, K. The impact of lead on bald eagles in New York from 1990-2018.
Interactive software:
Hanley, B, Dhondt, A, Dennis, B, & Schuler, K. 2019. EaglePOPd Web Interactive: Software to investigate the demography of Bald Eagles in the Northeast, USA from 1990- 2018 [Software]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/q4m1-se95
Hanley, B, Connelly, P, & Dennis, B. 2019. IsoPOPd: Interactive software to understand how elements in a population matrix model influence the asymptotic population growth rate [Software]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/bcmg-7w08
Hanley, B, Dhondt, A, Bunting, E, Pokras, M, Hynes, K, Forzán, M, & Schuler, K. 2019. CounterPOPd Web Interactive: Software to investigate the population scale impact of lead in bald eagles in the Northeast United States from 1990-2018 [Software]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/0v1k-wq39
Hanley, B, Dhondt, A, & Schuler, K. 2020. BandingPOPd: Software to investigate the USGS bald eagle banding and encounter data in the Northeast United States [Dataset]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/1n7f-xs53
Hanley, B, Dhondt, A, Bunting, E, Pokras, M, Hynes, K, Forzán, M, & Schuler, K. 2019. ClosedCounterPOPd Web Interactive: Software to investigate the population scale impacts of lead in hypothetically closed bald eagle populations [Software]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/q4t7-1y54
Hanley, B, Dhondt, A, Bunting, E, Pokras, M, Hynes, K, Forzán, M, & Schuler, K. 2019. DensiPOPd Web Interactive: Software to investigate the impacts to density dependence by lead in bald eagles in the Northeast United States [Software]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/6yb8-5c25
7 Hanley, B, Dhondt, A, Bunting, E, Pokras, M, Hynes, K, Forzán, M, & Schuler, K. 2019. ClosedDensiPOPd Web Interactive: Software to investigate the impacts to density dependence by lead in bald eagles in hypothetically closed systems [Software]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/n2x8-6p10
8 Hanley, B, Dhondt, A, Bunting, E, Pokras, M, Hynes, K, Forzán, M, & Schuler, K. 2019. PlastiPOPd Web Interactive: Software to investigate the life history plasticity in bald eagles in the Northeast United States [Software]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/7rxf-ee77
9 Hanley, B, Dhondt, A,Forzán, M, Bunting, E, Pokras, M, Hynes, K, Domínguez-Villegas, E, & Schuler, K. 2020. EagleDashboard: Assessing the population scale impacts of a disease, toxin, or contaminant in Bald Eagles [Software]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/0dm3-tf51
Data packages:
Avian Haven Wild Bird Rehabilitation Center. 2021. Avian Haven Bald Eagle Case Reports 2012-2019. Freedom, Maine [Data]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/qg9d-9p17
Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine. 2021. Tufts Bald Eagle Case Reports 1991-2019. Tufts University. North Grafton, Massachusetts [Data]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/6by1-j636
Hanley, B, Dhondt, A, Forzán, M, Bunting, E, Pokras, M, Hynes, K, Dominguez-Villegas, E, Ponce Cosio, A E, & Schuler, K.2021a. Veterinary Data Package: Lead in Bald Eagles in the Northeast United States [Data]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/3p9p-j249
Hanley, B, Dhondt, A, Forzán, M, Bunting, E, Pokras, M, Hynes, K, Dominguez-Villegas, E, Ponce Cosio, A E, & Schuler, K.2021b. Time Series Data Package: Lead in Bald Eagles in the Northeast United States [Data]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/wr25-4m46
United States Geological Survey National Wildlife Heath Center. 2021. National Wildlife Heath Center Bald Eagle Data 1963-2014. National Wildlife Health Center, Madison, Wisconsin [Data]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/jn80-e080
University of New Hampshire. 2021. New Hampshire Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory Bald Eagle Case Reports 2013-2017. University of New Hampshire. Durham, New Hampshire [Data]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/m8yz-1r93
Wildlife Health Center of Virginia. 2021. Wildlife Health Center of Virginia Bald Eagle Case Reports 2011-2017. WILD-ONe. Waynesboro, Virginia [Data]. Cornell University Library eCommons Repository. doi.org/10.7298/hyyc-ws65
Anderson, W (1992) Legislation & Lawsuits in The United States & Their Effects on Nontoxic Shot Regulations. Pages 56–60 In Pain DJ, Editor. Lead Poisoning in Waterfowl. Proceedings of An International Waterfowl & Wetlands Research. Bureau Workshop. International Waterfowl & Wetlands Research Bureau Special Publication 16: 56–60, Slimbridge, UK.
Anderson, D, Burnham, K, White, G (1994) AIC model selection in over dispersed capture-recapture data. Ecology, 75, 1780–1793.
Anderson, D, Burnham, K, & Thompson, W (2000) Null hypothesis testing: problems, prevalence, & an alternative. J. Wildlife Manage, 64, 912-923.
Anderson W, Havera S, Zercher B (2000) Ingestion of Lead & Nontoxic Shotgun Pellets by Ducks in The Mississippi Flyway. Journal of Wildlife Management 64:848–857.
Aalto, S, & Newsome, G (1980) Some methods of estimating the parameters of the Leslie Matrix using incomplete population data. Canadian Journal of Fisheries & Aquatic Sciences, 37, 1140-1148.
Abadi F, Gimenez, O, Arlettaz, R, & Schaub M (2010) An assessment of integrated population models: bias, accuracy, & violation of the assumption of independence. Ecology, 91(1): 7-14.
Aho, K, Derryberry, D, & Peterson, T (2014) Model selection for ecologists: the world views of AIC & BIC. Ecology 95, 631-636.
Akaike, H (1973) Information theory & an extension of the maximum likelihood principle. In B. N. Petrov & B. F. Csaki (Eds.), Second International Symposium on Information Theory, (pp. 267-281) Academiai Kiado, Budapest.
Akaike, H (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, AC-19, 716-723.
Alberts, S, & Altmann, J (2003) Matrix models for primate life history analysis. In - Primate life history & socioecology. University of Chicago Press. Chicago, Illinois, USA.
Alfano, D, & T Petit (1981) Behavioral Effects of Postnatal Lead Exposure: Possible Relationship to Hippocampal Dysfunction. Behavior & Neural Biology 32:319–333.
Alfonso, S, F Grousset, L Masse, & J Tastet (2001) A European Lead Isotope Signal Recorded From 6000 To 300 Years BP In Coastal Marshes (SW France) Atmospheric Environment 35:3595–3605.
Alvarez-Buylla, E, & Slatkin, M (1993) Finding confidence limits on population growth rates: Monte Carlo test of a simple analytic method. Oikos, 68:2, 221:224.
Alvarez-Buylla, E, & Slatkin, M (1994) Finding confidence limits on population growth rates: Three real examples revised. Ecology, 75:1, 255:260. .
Arnold, T (2010) Uninformative parameters & model selection using Akaike’s Information Criterion. Journal of Wildlife Management, 74, 1175–1178.
Arthur, W (1982) The ergodic theorems of demography; a simple proof. Demography, 19:4, 439-445.
Artmann, J, & E Martin (1975) Incidence of Ingested Lead Shot in Sora Rails. Journal of Wildlife Management 39:514–519.
Avery, D, & R Watson (2009) Regulation of Lead-Based Ammunition Around the World. In Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans (R. T. Watson, M. Fuller, M. Pokras, & W. G. Hunt, Editors) The Peregrine Fund, Boise, ID, USA. Pp. 161–167.
Barker, R & W Link (2015) Truth, models, model sets, AIC, & multimodel inference: a Bayesian perspective. J. Wildlife Manage, 79, 730–738.
Bartlett, M (1990) Chance or chaos? (with discussion) Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, A52, 321–347.
Basu, A, H Shioya, & C Park. 2011. Statistical Inference: The Minimum Distance Approach. Chapman & Hall (CRC Press)
Battaglia, A, S Ghidini, G Campanini, & R Spaggiari (2005) Heavy Metal Contamination in Little Owl (Athene Noctua) & Common Buzzard (Buteo Buteo) From Northern Italy. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety 60:61–66.
Bauer, J, K Logan, L Sweanor, & W Boyce (2005) Scavenging Behavior in Puma. Southwestern Naturalist 50: 466–471.
Bedrosian B, Craighead D, Crandall R (2012) Lead Exposure in Bald Eagles from Big Game Hunting, The Continental Implications & Successful Mitigation Efforts. Plos ONE 7: E51978.
Bellinger, D, J Burger, T Cade, D Cory-Slechta, M Finkelstein, H Hu, M Kosnett, P Landrigan, B Lanphear, M Pokras, P Redig, B Rideout, et al (2013) Health Risks from Lead-Based Ammunition in The Environment. Environmental Health Perspectives 121: A178–A179.
Bellrose, F (1959) Lead Poisoning as a Mortality Factor in Waterfowl Populations. Illinois Natural History Survey Bulletin 27:235–288.
Bennett, J, C Kaufman, I Koch, J Sova, & K Reimer (2007) Ecological Risk Assessment of Lead Contamination at Rifle & Pistol Ranges Using Techniques to Account for Site Characteristics. Science of The Total Environment 374:91–101.
Benson, P, I Plug, & J Dobbs (2004) An Analysis of Bones & Other Materials Collected by Cape Vultures at The Kransberg & Blouberg Colonies, Limpopo Province, South Africa. Ostrich 75: 118–132.
Benson, W, B Pharaon, & P Miller (1974) Lead Poisoning in A Bird of Prey. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination Toxicology 11:105–108.
Bent, A (1937) Smithsonian Institution United States National Museum Bulletin 167 (Part 1): 321-333. United States Government Printing Office.
Bernardelli, H (1941) Population waves. Journal of Burma Research Society, 31, 1-18.
Berryman, A & Lima, M (2006) Deciphering the effects of climate on animal populations: diagnostic analysis provides new interpretation of Soay sheep dynamics. American Naturalist, 168, 784–795.
Best, T, T Garrison, & C Schmitt (1992) Availability & Ingestion of Lead Shot by Mourning Doves (Zenaida Macroura) In Southeastern New Mexico. Southwestern Naturalist 37: 287–292.
Beyer, W (ed.) 1978. Algebra. – In: CRC handbook of mathematical sciences. CRC Press, 69-72. Boca Raton, Florida, USA.
Beyer W, Spann J, Sileo L, Franson J (1988) Lead Poisoning in Six Captive Avian Species. Arch Environ Contain Toxicology 17:121–130.
Beyer, W, J Dalgarn, S Dudding, J French, R Mateo, J Miesner, L Sileo, & J Spann (2004) Zinc & Lead Poisoning in Wild Birds in The Tri-State Mining District (Oklahoma, Kansas, & Missouri) Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 48:108–117.
Beyer, W, J Franson, J French, T May, B Rattner, V Shearn-Bochsler, S Warner, J Weber, & D Mosby (2013) Toxic Exposure of Songbirds to Lead in The Southeast Missouri Lead Mining District. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 65:598–610.
Birdlife International. 2008. Species Factsheets Downloaded on 29 May 2008.
Bjerregaard, P, P Johansen, G Mulvad, H Pedersen, & J Hansen (2004) Lead Sources in Human Diet in Greenland. Environmental Health Perspectives 112:1496–1498.
Bloom, P, J Scott, O Pattee, & M Smith (1989) Lead Contamination of Golden Eagles (Aquila Chrysaetos) Within the Range of The Californian Condor (Gymnogyps Californianus) Pages 481–482 In B-U. Meyburgh & R.D. Chancellor (Eds.) Raptors in The Modern World. Proceedings of the 3rd World Conference on Birds of Prey & Owls, Eliat, Israel, 22–27 March 1987. World Working Group on Birds of Prey, Berlin, London, & Paris.
Blus, L, C Henny, D Hoffman, L Sileo, & D. J. Audet (1999) Persistence of High Lead Concentrations & Associated Effects in Tundra Swans Captured Near A Mining & Smelting Complex in Northern Idaho. Ecotoxicology 8:125– 132.
Blus, L (2011) DDT, DDD, & DDE In Birds. In Environmental Contaminants in Biota: Interpreting Tissue Concentrations, Second Edition (W. N. Beyer & J. P. Meador, Editors) CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA. Pp. 425–444.
Boggess, W (Editor) (1977) Lead in The Environment. Report NSF/RA-770214. National Science Foundation, Washington, DC, USA. Brennan, L. A (1991) How Can We Reverse the Northern Bobwhite Population Decline? Wildlife Society Bulletin 19: 544–555.
Bolen, E, & Robinson, W (1999) - In: Wildlife Ecology & Management. 5th Ed. Pearson, London, United Kingdom.
Bortolotti, G (1984a) Sexual dimorphism & age-related size variation in Bald Eagles. Journal of Field Wildlife Management, 48, 72-81.
Bortolotti, G (1984b) Criteria for determining age & sex of nestling Bald Eagles. Journal of Field Ornithology, 55, 467-481.
Bortolotti, G (1986) Evolution of Growth Rates in Eagles: Sibling Competition Vs. Energy Considerations. Ecology, 67:1, 182-194.
Box, G & Tiao, G (1973) Bayesian Inference in Statistical Analysis. Addison-Wesley, Reading, Mass.
Box, G (1979), "Robustness in the strategy of scientific model building", in Launer, R. L.; Wilkinson, G. N, Robustness in Statistics, Academic Press, pp. 201–236.
Bozdogan, H (1987) Model selection & Akaike's information criterion (AIC): the general theory & its analytical extensions. Psychometrika 52, 345-370.
Bratton, G, & D Kowalczyk (1989) Lead Poisoning. In Current Veterinary Therapy VII, R. W. Kirk (Ed.) W. B. Saunders Company Ltd, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, Pp. 141–144.
Bruggeman, J, Route, W, Redig, P, & Key R (2018) Pattern & trends in lead (Pb) concentrations in bald eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus) nestlings from the wester Great Lakes region. Ecotoxicology 27: 605-618.
Buehler, D, Fraser, J, Seeger, Therres, J, & Byrd, M (1991) Survival rates & population dynamics of Bald Eagles on Chesapeake Bay. Journal of Wildlife Management, 55, 608–613.
Buehler, D, Mersmann T, Fraser, J, Janis, K, Seegar, J (1991b) Differences In Distribution Of Breeding, Nonbreeding, & Migrant Bald Eagles On The Northern Chesapeake Bay. The Condor, 93, 399-408.
Buehler, D (2000) Bald Eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus), version 2.0. In – The Birds of North America (A. F. Poole & F. B. Gill, Editors) Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA.
Buekers, J, E Redeker, & E Smolders (2009) Lead Toxicity to Wildlife: Derivation of A Critical Blood Concentration for Wildlife Monitoring Based on Literature Data. Science of The Total Environment 407:3431–3438.
Bull, K, W Every, P Freestone, J Hall, & D Osborn (1983) Alkyl Lead Pollution & Bird Mortalities on The Mersey Estuary, UK 1979–1981. Environmental Pollution 31: 239–259.
Burco, J, Myers, A, Schuler, K, & Gillin, C (2012) Acute Lead Toxicosis via Ingestion of Spent Ammunition in a Free-Ranging Cougar (Puma concolor) Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 48(1): 216-219.
Burger, J, & M Gochfeld (1994) Behavioral Impairments of Lead-Injected Young Herring Gulls in Nature. Fundamental & Applied Toxicology 23:553–561.
Burger J (1995) A Risk Assessment for Lead in Birds. J Toxicology Environ Health 45:369–396.
Burger, J, & M Gochfeld (2000) Effects of Lead on Birds (Laridae): A Review of Laboratory & Field Studies. Journal of Toxicology & Environmental B 3:59–78.
Burger, J, & M Gochfeld (2004) Metal Levels in Eggs of Common Terns (Sterna Hirundo) In New Jersey: Temporal Trends From 1971 To 2002. Environmental Research 94:336– 343.
Burgman M, Ferson S, & Akcakaya H (1993) Risk assessment in conservation biology. Chapman & Hall. London, United Kingdom.
Burnham K, Anderson D (2002) Model Selection & Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach, 2nd Edn. Springer, New York
Butler, D, R Sage, R Draycott, J Carroll, & D Potts (2005) Lead Exposure in Ring-Necked Pheasants on Shooting Estates in Great Britain. Wildlife Society Bulletin 33: 583–589.
Caceres, M, & Caceres-Saez, I (2013) Calculating effective growth rate from a random Leslie model: Application to incidental mortality analysis. Ecological Modelling, 251, 312-322.
Cade, B (2015) Model averaging & muddled multimodel inferences. Ecology, 96, 2370‑2382.
Cade, T (2007) Exposure of California Condors to Lead from Spent Ammunition. Journal of Wildlife Management, 71:2125– 2133.
Calvert, J (1876) Pheasants Poisoned by Swallowing Shots. The Field 47:189.
Campbell, H (1950) Quail Picking Up Lead Shot. Journal of Wildlife Management 14:243–244.
Canfield R, Henderson C Jr, Cory-Slechta D, et al. Intellectual Impairment in Children with Blood Lead Concentrations Below 10 Jig Per Deciliter. New Engl J Med. 2003; 348:1517-1526. 14.
Carpenter, J, O Pattee, S Fritts, B Rattner, S Wiemeyer, J Royle, & M Smith (2003) Experimental Lead Poisoning in Turkey Vultures (Cathartes Aura) Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 39:96–104.
Carr, E, M Lee, K Marin, C Holder, M Hoyer, M Pedde, R Cook, & J Touma (2011) Development & Evaluation of An Air Quality Modeling Approach to Assess Near-Field Impacts of Lead Emissions from Piston-Engine Aircraft Operating on Leaded Aviation Gasoline. Atmospheric Environment, 45:5795– 5804.
Case & Associates (2006) Non-Toxic Shot Regulation Inventory of The United States & Canada. Final Report to The Ad Hoc Mourning Dove & Lead Toxicosis Working Group. D Case & Associates, Mishawaka, IN, USA.
Case, T (2000) – In: An illustrated guide to theoretical ecology. Oxford University Press, New York, New York, USA.
Castrale, J (1989) Availability of Spent Lead Shot in Fields Managed for Mourning Dove Hunting. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 17:184–189.
Caswell, H (2001) Matrix population models: Construction, analysis, & interpretation. 2nd edition. Sunderland: Sinauer Associates.
Caswell, H, Brault, S, Read, A, & Smith, T (1998) Harbor porpoise & fisheries: an uncertainty analysis of incidental mortality. Ecological Applications, 8:4, 1226-1238.
Caswell, H (2007) Sensitivity analysis of transient population dynamics. Ecology Letters, 10:1, 1-15.
Caswell, H, & Neubert, M (2007) Reactivity & transient dynamics of discrete-time ecological systems. Journal of Difference Equations & Applications, 2, pgs. 295-310.
Caswell, H (ed.) 2009. -In: Advances in Ecological Research. Vol. 41. Elsevier. Academic Press. Amsterdam, Netherlands.
Centers for Disease Control (2013) Blood Lead Levels in Children Aged 1–5 Years—United States, 1999–2010. Morbidity & Mortality Weekly Report 62 (April 5):245–248.
Chang, G, B Davis, C Stringfield, & C Lutz (2007) Prospective Immunization of The Endangered California Condors (Gymnogyps Californianus) Protects This Species from Lethal West Nile Virus Infection. Vaccine 25: 2325– 2330.
Charlesworth, B (2009) Effective population size & patterns of molecular evolution & variation. Genetics, 10, pgs. 195-205.
Chatfield, C (1995) Model Uncertainty, Data Mining & statistical Inference. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series A (Statistics in Society) 158:419-466.
Chen, I (2013) Overlooked: Thousands of Americans Exposed to Dangerous Levels of Lead in Their Jobs. Scientific American 309(3).
Choi, Y, Tegzes, J, & Thurmond, M (2004) Influence of Age, Sex, & Production Class on Liver Zinc Concentration in Calves. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation 16: 278–282.
Church, M, R Gwiazda, R Risebrough, K Sorenson, C Chamberlain, S Farry, W Heinrich, B Rideout, & D Smith (2006) Ammunition is the Principal Source of Lead Accumulated by California Condors Re-Introduced to The Wild. Environmental Science & Technology 40:6143–6150.
Claeskens, G & Hjort, N (2008) Model Selection & Model Averaging. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. Edwards, A1972. Likelihood. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Clark A, Scheuhammer A (2003) Lead Poisoning in Upland Foraging Birds of Prey in Canada. Ecotoxicology 12:23–30
Clausen, B, & C Wolstrup (1979) Lead Poisoning in Game from Denmark. Danish Review of Game Biology 11:22.
Clausen, B, K Elvestad, & O Karlog (1982) Lead Burden in Mute Swans from Denmark. Nordisk Veterinary Medicine 34:83–91.
Cornatzer W, Fogarty E, Cornatzer E (2007) Qualitative & Quantitative Detection of Lead Fragments in Random Venison Packages Donated to The Community Action Food Centers Of North Dakota. In: Watson R, Fuller M, Pokras M, Hunt W, Eds. Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans. Boise, ID: The Peregrine Fund; 2009:154-156. 20.
Costantino, R, & Desharnais, R (1981) Gamma distributions of adult numbers for Tribolium populations in the region of their steady states. Journal of Animal Ecology, 50, 667–681.
Costantino, R, Desharnais, R, Cushing, J, & Dennis, B (1997) Chaotic dynamics in an insect population. Science, 275, 389–391.
Coulson, T, Catchpole, E, Albon, S, Morgan, B, Pemberton, J, Clutton-Brock, T. et al (2001) Age, sex, density, winter weather, & population crashes in Soay sheep. Science, 292, 1528–1531.
Craig, T, J Connelly, E Craig, & T Parker (1990) Lead Concentrations in Golden & Bald Eagles. Wilson Bulletin 102: 130–133.
Craighead, D, & B Bedrosian (2008) Blood Lead Levels of Common Ravens with Access to Big-Game Offal. Journal of Wildlife Management 72:240–245.
Crone E, Ellis M, Morris W, Stanley A, Bell T, Bierzychudek P, Ehrlen J, Kaye T, Knight T, Lesica P, Oostermeijer G, Quintana-Ascencio P, Ticktin T, Valverde T, Williams J, Doak D, Ganesan R, McEachern K, Thorpe A, & Menges E (2012) Ability of matrix models to explain the past & predict the future of plant populations. Conservation Biology, 27(5), 968-978.
Crouse, D, Crowder, L, & Caswell, H (1987) A stage-based population model for loggerhead sea turtles & implications for conservation. Ecology, 86:5, 1412-1423.
Cruz-Martinez L, Redig P, Deen J (2012) Lead from Spent Ammunition: A Source of Exposure & Poisoning in Bald Eagles. Human Wildlife Interaction 6:94–104.
Cryer, M, J Corbett, & M Winterbotham (1987) The Deposition of Hazardous Litter by Anglers at Coastal & Inland Fisheries in South Wales. Journal of Environmental Management 25:125–135.
Cull, P, & Vogt, A (1973) Mathematical analysis of the asymptotic behavior of the Leslie population matrix model. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 35, 645-661.
Custer, T, J Franson, & O Pattee (1984) Tissue Lead Distribution & Hematologic Effects in American Kestrels (Falco Sparverius) Fed Biologically Incorporated Lead. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 20: 39–43.
Delia, J, & S Haig (2013) California Condors in The Pacific Northwest. Oregon State University Press, Corvallis, OR, USA.
Dalal, S & Hall, W (1983) ”Approximating Priors by Mixtures of Natural Conjugate Priors” J. R. Statist. Soc, B, 45, 278-286.
Danvir, R, & F Lendzey (1981) Feeding Behavior of a Captive Cougar on Mule Deer. Encyclia, 58: 50–56.
Dawe, N (2016) Cooperative breeding by the Bald Eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus) on Vancouver Islands, British Columbia, British Columbia Birds, 26, 35-40.
De Francisco, N, J Ruiz Troya, & E Aguera (2003) Lead & Lead Toxicity in Domestic & Free-Living Birds. Avian Pathology 32: 3–13.
de Kroon, H, van Groenendael, J, & Ehrlen, J (2000) Elasticities: a review of methods & model limitations. Ecology, 81, 607-618.
Decker, R, A Mcdermid, & J Prideaux (1979) Lead Poisoning in Two Captive King Vultures. Journal of The American Medical Association 175:1009.
Deem S, Terrell S, Forrester D (1998) A Retrospective Study of Morbidity & Mortality of Raptors in Florida: 1988–1994. J Zoo Wildl Med 29:160–164.
Deevey, E (1947) Life tables for natural populations of animals. Quarterly Review of Biology, 22, 283-314.
Demartini J, Wilson A, Powell J, Powell C (2001) Lead Arthropathy & Systemic Lead Poisoning from An Intra articular Bullet. American Journal of Roentgenology 176(5):1144–1144.
Dement, S, J Chisolm, Jr, M Eckhaus, & J StrandBerg (1987) Toxic Lead Exposure in The Urban Rock Dove. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 23:273–278.
Demichele, S (1984) Nutrition of Lead. Comparative Biochemistry & Physiology A 78:401–408.
Dennis, B (2013) – In: The R student companion. CRC Press. Boca Raton, Florida, USA.
Dennis, B, & Costantino, R (1988) Analysis of steady-state populations with the gamma abundance model: application to Tribolium. Ecology, 69, 1200-1213.
Dennis, B, & Taper, M (1994) Density dependence in time series observations of natural populations: estimation & testing. Ecological Monographs, 64, 205-224.
Dennis, B, Desharnais, R, Cushing, J, & Costantino, R (1995) Nonlinear demographic dynamics: mathematical models, statistical methods, & biological experiments. Ecological Monographs, 65, 261–281.
Dennis, B, Desharnais, R, Cushing, J, Hensen, S, & Costantino R (2001) Estimating chaos & complex dynamics in an insect population. Ecological Monographs, 71, 277-303.
Department of The Interior (DOI) (2007) Endangered & Threatened Wildlife & Plants: Removing the Bald Eagle in The Lower 48 States from The List of Endangered & Threatened Wildlife. Fed Reg 72:37346–37372
Dermody, B, C Tanner, & A Jackson (2011) The Evolutionary Pathway to Obligate Scavenging in Gyps Vultures. Plos ONE 6(9): E24635.
Devenish-Nelson, E, Harris, S, Soulsbury, C, Richards, S, & Stephens, P (2010) Uncertainty in population growth rates. Determining confidence intervals from point estimates of parameters. PlosOne, 5:10, e13628.
Dey, P, J Burger, M Gochfeld, & K Reuhl (2000) Developmental Lead Exposure Disturbs Expression of Synaptic Neural Cell Adhesion Molecules in Herring Gull Brains. Toxicology 146:137–147.
Dhondt, A, & Eycherman, R (1980) Competition & regulation of numbers in Great & Blue Tit. Ardea, 68, 121-132.
Dhondt, A (1993) Interspecific Competition in Birds. Oxford University Press, Oxford, United Kingdom.
Ding, H, Trajcevski, G, Scheuermann, P, Wang, X, & Keogh, E (2008) Querying & mining of time series data: Experimental comparison of representations & distance measures. Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, 1, 1542-1552.
Dinsmore, S, & Johnson, D (2012) In - Silvy (Ed.), The wildlife techniques manual. Johns Hopkins University Press. Baltimore, Maryland, USA.
Diters, R, & S Nielsen (1978) Lead Poisoning of Raccoons in Connecticut. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 14: 187–192.
Doak, D, Kareiva, P, & Klepetka, B (1994) Modeling population viability for the desert tortoise in the western Mojave Desert. Ecological Applications, 4, 446-460.
Dohoo, I (2014) Bias – Is it a problem, & what should we do? Preventative Veterinary Medicine, Vol 113, pgs. 331-337.
Donazar, J, C Palacios, L Gangoso, O Ceballos, M Gonzalez, & F Hiraldo (2002) Conservation Status & Limiting Factors in The Endangered Population of Egyptian Vulture (Neophron Percnopterus) In the Canary Islands. Biological Conservation 107:89–97.
Duerr, A (1999) Abundance of Lost & Discarded Fishing Tackle & Implications for Waterbird Populations in The United States. M.S. Thesis, School of Renewable Natural Resources, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA.
Duke G, Evanson, O, Jegers, A (1976) Meal to Pellet Intervals In 14 Species of Captive Raptors. Comp Biochem Physiol 53A:1–6.
Dunne, P (2006) Pete Dunne's essential field guide companion. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, New York, USA.
Dutton, C, & E Bolen (2000) Fall Diet of a Relict Pheasant Population In North Carolina. Journal of The Elisha Mitchell Scientific Society 116:41–48.
Edens, F, & J Garlich (1983) Lead-Induced Egg Production Decrease in Leghorn & Japanese Quail Hens. Poultry Science 62:1757–1763.
Eisler, R (1986) Polychlorinated Biphenyl Hazards to Fish, Wildlife, & Invertebrates: A Synoptic Review. U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Biological Report 85(1.7)
Eisler, R (1988) Lead Hazards To fish, Wildlife, & Invertebrates: A Synoptic Review, Contaminant Hazard Reviews, Report Number 14, US Fish & Wildlife Service. Patuxent Wildlife Research Center, Laurel, MD.
Eisler, R (2000) Handbook of Chemical Risk Assessment: Health Hazards to Humans, Plants, & Animals, Vol 1. Metals. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton Fournier.
Elandt, R, & Johnson, N (1980) - In: Survival models & data analysis. John Wiley & Sons, New York, New York, USA.
Elder, W (1955) Fluoroscope Measures of Hunting Pressure in Europe & North America. Transactions of The North American Wildlife Conference 20: 298–322.
Elliot, J, Langelier, K, Scheu-Hammer, A, Sinclair, P, & P White-Head (1992) Incidence of Lead Poisoning in Bald Eagles & Lead Shot in Waterfowl Gizzards from British Columbia 1988–1991. Canadian Wildlife Service Progress Notes. Canadian Wildlife Service, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada.
Endangered Species Act (1973) 16 U.S.C. 1531-1544, 87 Stat. 884.
Epps, C (2014) Considering the Switch: Challenges of Transitioning to Non-Lead Hunting Ammunition. Condor 116: 429–434.
Ersoy, Y, & Moscardini, A (1994) In – Mathematical modelling courses for engineering education. Springer-Verlag. Berlin, Germany.
European Commission (2004) Advantages & Drawbacks of Restricting the Marketing & Use of Lead in Ammunition, Fishing Sinkers, & Candle Wicks. Final Report. European Commission, Enterprise Directorate-General.
Ezard, T, Bullock, J, Dalgleish, H, Million, A, Pelletier, F, Ozgul, A, & Koons, D (2010) Matrix models for a changeable world: the importance of transient dynamics in population management. Journal of Applied Ecology, 47, 515-523.
Fair, J, & O Myers (2002) The Ecological & Physiological Costs of Lead Shot & Immunological Challenge to Developing Western Bluebirds. Ecotoxicology 11:199–208.
Fair, J, & R Ricklefs (2002) Physiological, Growth, & Immune Response of Japanese Quail Chicks to The Multiple Stresses of Immunological Challenge & Lead Shot. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 42:77–87.
Falandysz, J, Jakuczun, B, & T Mizera (1988) Metal & Organochlorines in Four Female White-Tailed Eagles. Marine Pollution 19:521– 526.
Ferrandis, P, R Mateo, F Lopez-Serrano, M Martinez-Haro, & E Martinez-Duro (2008) Lead Shot Exposure in Red legged Partridge (Alectoris Rufa) On A Driven Shooting Estate. Environmental Science & Technology 42:6271–6277.
Ferrer, M (2001) The Spanish Imperial Eagle. Lynx Editions, Barcelona, Spain.
Ferrer, M, Otalora, F, & Garcia-Ruiz, J (2004) Density-dependent age of first reproduction as a buffer affecting persistence of small populations. Ecological Applications, 14:2, 616-624.
Ferrer, M, V Penteriani, J Balbontin, & M PandOlfi (2003) The Proportion of Immature Breeders as a Reliable Early Warning Signal of Population Decline: Evidence from The Spanish Imperial Eagle in Donana. Biological Conservation 114:463–466.
Finkelstein, M, Gwiazda, R, & D Smith (2003) Lead Poisoning of Seabirds: Environmental Risks from Leaded Paint at a Decommissioned Military Base. Environmental Science & Technology 37:3256–3260.
Finkelstein, M, D George, S Scherbinski, R Gwiazda, M Johnson, J Burnett, J Brandt, S Lawrey, A Pessier, M Clark, J Wynne, J Grantham, & D Smith (2010) Feather Lead Concentrations & (207)Pb/(206)Pb Ratios Reveal Lead Exposure History of California Condors (Gymnogyps Californianus) Environmental Science & Technology 44:2639–2647.
Finkelstein, M, D Doak, D George, J Burnett, J Brandt, M Church, J Grantham, & D Smith (2012) Lead Poisoning & The Deceptive Recovery of The Critically Endangered California Condor. Proceedings of The National Academy of Sciences USA 109:11449–11454.
Firestone, S, Lewis, F, Schemann, K, Ward, M, Toribio, J, & Dhand, N (2013) Navneet K. Dhand Understanding the associations between on-farm biosecurity practice & equine influenza infection during the 2007 outbreak in Australia. Preventative Veterinary Medicine, 110(1): 28-36.
Fisher, I, D Pain, & V Thomas (2006) A Review of Lead Poisoning from Ammunition Sources in Terrestrial Birds. Biological Conservation 131:421–432.
Fix, A, Barrows, S (1990) Raptors Rehabilitated in Iowa During 1996 & 1997: A Retrospective Study. J Wildl Dis 26:18–21
Flint, P, & J Schamber (2010) Long-Term Persistence of Spent Lead Shot in Tundra Wetlands. Journal of Wildlife Management 74:148–151.
Flora, S, G Flora, & G Saxena (2006) Environmental Occurrence, Health Effects & Management of Lead Poisoning. In Lead: Chemistry, Analytical Aspects, Environmental Impacts & Health Effects (S. B. Cascas & J. Sordo, Editors) Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. Pp. 158–228.
Fox, G, & Gurevitch, J (2000) Population numbers count: tools for near-term demographic analysis. American Naturalist, 156, 242–256.
Fox, J (2016) Applied regression analysis & generalized linear models. 2nd edition. Sage Publications Inc. Los Angeles, California, USA.
Frank, A (1986) Lead Fragments in Tissues from Wild Birds: A Cause of Misleading Analytical Results. Sci Total Environ 54:275–281.
Frankham, R (2005) Genetics & extinction. Biological Conservation, 126, 131-140.
Franson, J, L Sileo, O Pattee, & J Moore (1983) Effects of Chronic Dietary Lead in American Kestrels (Falco Spaverius) Journal of Wildlife Diseases 19:110–113.
Franson, J (1996) Interpretation of Tissue Lead Residues in Birds Other Than Waterfowl. Pages 265–279 In W. N. Beyer, G. H. Heinz, & A. W. Redmon-Norwood (Eds.) Environmental Contaminants in Wildlife: Interpreting Tissue Concentrations. SETAC, CRC/Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Florida, USA.
Franson, J, N Thomas, M Smith, A Robbins, S Newman, & P Mccartin (1996) A Retrospective Study of Post-Mortem Findings in Red-Tailed Hawks. Journal of Raptor Research 30: 7–14.
Franson, J, Smith, M (1999) Poisoning of Wild Birds from Exposure to Anticholinesterase Compounds & Lead: Diagnostic Methods & Selected Cases. Seminars Avian Exotic Pet Med 8:3–11
Franson, J, S Hansen, T Creekmore, C Brand, D Evers, A Duerr, & S Destefano (2003) Lead Fishing Weights & Other Fishing Tackle in Selected Waterbirds. Waterbirds 26:345–352.
Franson, J, Hansen S, Schultz J (2009) Ingested Shot & Tissue Lead Concentrations in Mourning Doves. Pages 175–186 In Watson RT, Fuller M, Pokras M, Hunt WG, Editors. Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans. Boise, Idaho: The Peregrine Fund.
Franson, J, & D Pain (2011) Lead in Birds. In Environmental Contaminants in Biota: Interpreting Tissue Concentrations, Second Edition (W. N. Beyer & J. P. Meador, Editors) Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, FL, USA. Pp. 563–593.
Franson, J, Russell, R (2014) Lead & Eagles: Demographic & Pathological Characteristics of Poisoning, & Exposure Levels Associated with Other Causes of Mortality. Ecotoxicology 23:1722–1731.
Frenzel, R, & R Anthony (1989) Relationship of Diets & Environmental Contaminants in Wintering Bald Eagles. Journal of Wildlife Management 53:792–802.
Frey, S, S Majors, M Conover, T Messmer, & D Mitchell (2003) Effect of Predator Control on Ring-Necked Pheasant Populations. Wildlife Society Bulletin 31:727–735.
Friedrichs, K, Harr K, Freeman K, Szladovits, B, Walton R, Barnhart, K, Blanco-Chavez J (2012) Preference Interval Guidelines: Determination Of De Novo Reference Intervals in Veterinary Species & Other Related Topics. American Society for Veterinary Clinical Pathology. 41(4):441–53.
Friend, M (1987) Field Guide to Wildlife Diseases. United States Fish & Wildlife Service, Washington, DC, USA.
Friend, M (1999) Lead. In Field Manual of Wildlife Diseases: General Field Procedures & Diseases of Birds, E. A. Ciganovich (Ed.) Information & Technology Report, 1999-001 ADA371843/Ll US Geological Survey, Biological Resources Division, Madison, Wisconsin, Pp. 317–334.
Friend, M, Franson J, Ciganovich E (1999) Field Manual of Wildlife Diseases. Chapter 43. U.S. Department of The Interior, U.S. Geological Survey, Washington, D.C.
Friend, M, Franson J, Anderson W (2009) Biological & Societal Dimensions of Lead Poisoning in Birds in the USA. In: Watson RT, Fuller M, Pokras M, Hunt WG (Eds) Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans. The Peregrine Fund, Boise, Pp 34–60.
Fry, M, K Sorenson, J Grantham, J Burnett, J Brant, & M Koenig (2009) Lead Intoxication Kinetics in Condors from California. Abstract in R. T. Watson, M. Fuller, M. Pokras, & W. G. Hunt (Eds.) Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans. The Peregrine Fund, Boise, Idaho, USA.
Fryxell, J, Sinclair, A, & Caughley, G (2014) In - Wildlife ecology, conservation, & management. 3rd edition. Johns Wiley & Sons. Hoboken, New Jersey, USA.
Fujiwara, M, & Caswell, H (2002) Estimating population projection matrices from multi-stage mark-recapture data. Ecology, 83, 3257-3265.
Fuller M, Pokras M, Hunt WG, Eds. Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans. Boise, ID: The Peregrine Fund; 2009:240-253. 15.
Futuyma, D (2009) Evolution. 2nd ed. Sinuaer & Associates. Sunderland, Massachusetts, USA.
Gallardo, J, Vilella, F, & Colvin, M (2019) A seasonal population matrix model of the Caribbean Red-tailed Hawk Bueo jamaicensis in eastern Puerto Rico. Ibis, 161, 459-466.
Garcelon D (1990) Observations of Aggressive Interactions by Bald Eagles of Known Age & Sex. Condor 92:532–534
Garcelon, D, Slater, G, Danilson, C (1995) Cooperative nesting by a trio of Bald Eagles. Journal of Raptor Research, 29:3, 210-213.
Garcia-Fernandez, A, E Martinez-Lopez, D Romero, P Maria-Mojica, A Godino, & P Jimenez (2005) High Levels of Blood Lead in Griffon Vultures (Gyps Fulvus) From Cazorla Natural Park (Southern Spain) Environmental Toxicology 20: 459–463.
Garlick, M, Powell, J, Hooten, M, & McFarlane, L (2011) Homogenization of large-scale movement models in ecology. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology. 73, pgs. 2088-2108.
Geffory A, Friedrichs K, Harr K, Concordet D, Trumel C, Braun JP (2009) Reference Values: A Review. Vet Clin Pathol. 38(3):288–298.
Gelman, A, Hill, J, & Yajima, M (2012) Why we (usually) don't have to worry about multiple comparisons. Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness, 5, 189-211.
Gerber, B, & Kendall, W (2016) Considering transient population dynamics in the conservation of slow life-history species: An application to the sandhill crane. Biological Conservation, 200, 228.
Gerrard, J, Gerrard, P. Bortolotti, G. & Dzus, E (1992) A 24-year study of Bald Eagles on Besnard Lake, Saskatchewan. Journal of Raptor Research, 26, 159-166.
Gerrodette, T (2011) Inference without significance: measuring support for hypotheses rather than rejecting them. Marine Ecology: An Evolutionary Perspective, 32, 404–418.
Gerstenberger, S, & D Divine (2006) Lead Shot Deposition & Distribution in Southern Nevada. Journal of The Nevada Public Health Association 3:8–13.
Gill, E, & K Langelier (1994) Acute Lead Poisoning in A Bald Eagle Secondary to Bullet Ingestion. Canadian Veterinary Journal 35:303– 304.
Gilroy, J, Virzi, T, Boulton, R, & Lockwood, J (2012) A new approach to the “apparent survival” problem: Estimating true survival rates from mark-recapture studies. Ecology, 93:7, 509-1516.
Gilsleider E, Oehme F (1982) Some Common Toxicosis in Raptors. Veterinary & Human Toxicology 24:169.
Goddard, C, N Leonard, D Stang, P Wingate, B Rattner, J Franson, & S Sheffield (2008) Management Concerns About Known & Potential Impacts of Lead Use in Shooting & In Fishing Activities. Fisheries 33:228–236.
Golden N, Warner S, Coffey M (2016) A Review & Assessment of Spent Lead Ammunition & Its Exposure & Effects to Scavenging Birds in The United States. Pages 123–191 In P. De Voogt, Editor. Reviews of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology. Volume 237. Basel, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing.
González, L, & F Hiraldo (1988) Organochlorine & Heavy Metals Contamination in The Eggs of The Spanish Imperial Eagle (Aquila Adalberti) & Accompanying Changes in Eggshell Morphology & Chemistry. Environmental Pollution 51:241–258.
Goodman D (2004) Methods for joint inference from multiple data sources for improved estimates of population size & survival rates. Mar Mam Sci 20:401–423.
Gotelli, N (2004) - In: A Primer of ecology. Sinuaer Associates, Inc. Sunderland, Massachusetts, USA.
Goyer, R (1996) Toxic Effects of Metals. In Casarett & Doull’s Toxicology: The Basic Science of Poisons, Fifth Edition (C. D. Klaassen, M. O. Amdur, & J. Doull, Editors) McGraw Hill, New York, NY, USA. Pp. 691–736.
Grand, J, P Flint, M Petersen, & C Moran (1998) Effect of Lead Poisoning on Speckled Eider Survival Rates. Journal of Wildlife Management 62:1103–1109.
Grandjean, P (1976) Possible Effect of Lead on Eggshell Thickness in Kestrels 1874–1974. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 16:101–106.
Grade, T (2011) Effects of Lead Fishing Tackle on Common Loons (Gavia Immer) In New Hampshire. M.S. Thesis, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, USA.
Grantham, J (2007) Reintroduction of California Condors into Their Historical Range: The Recovery Program in California. In California Condors in the 21st Century, A Mee, L Hall & J Grantham (Eds.) Series in Ornithology, No. 2. American Ornithologists Union, Washington, DC, & Nuttall Ornithological Club, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Pp. 123–138.
Grasman, K & P Scanlon (1995) Effects of Acute Lead Ingestion & Diet on Antibody & T-Cell-Mediated Immunity in Japanese Quail. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 28:161–167.
Graur, D, & Li, W (2000) Dynamics of genes in populations. In – Fundamentals of molecular evolution. 2nd edition. Sinuaer Associates Inc. Sunderland, Massachusetts, USA.
Green, R, W Hunt, C Parish, & I Newton (2009) Effectiveness of Action to Reduce Exposure of Free-Ranging California Condors in Arizona & Utah To Lead from Spent Ammunition. In Proceedings of The Conference: Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans, R Watson, M Fuller, M Pokras & G Hunt (Eds.) The Peregrine Fund, Boise, Idaho, Pp. 240–253.
Gregory, R, N Wilkinson, D Noble, J Robinson, A Brown, J Hughes, D Procter, D Gibbons, & C Gal– Braith (2002) The Population Status of Birds in The United Kingdom, Channel Islands & Isle of Man: An Analysis of Conservation Concern 2002–2007. British Birds 95:410–48.
GriER, J (1980) Modeling approaches to Bald Eagle population dynamics. Wildlife Society Bulletin, 8, 316-322.
Griffin, C, Baskett T, Sparrowe R (1980) Bald Eagles & The Management Program at Swan Lake National Wildlife Refuge. Trans N Am Wildl Nat Resour Conf 45:252–262.
Grinnell, B (1894) Lead Poisoning. For Stream 42:117–118.
Grueber, C, Nakagawa, S, Laws, R, & Jamieson, I (2011) Multimodel inference in ecology & evolution: challenges & solutions. J. Evolutionary Biology, 24, 699-711.
Grund, M, Cornicelli L, Carlson L, Butler E (2010) Bullet Fragmentation & Lead Deposition in White-tailed Deer & Domestic Sheep. Human-Wildlife Interactions 4:257–265.
Guitart, R, J Serratosa, & V Thomas (2002) Lead-Poisoned Wildfowl in Spain: A Significant Threat for Human Consumers. International Journal of Environmental Health Research 12:301–309.
Gustavsson, P, & L Gerhardsson (2005) Intoxication from An Accidentally Ingested Lead Shot Retained in The Gastrointestinal Tract. Environmental Health Perspectives 113:491–493.
Guthery, F, Brennan, L, Peterson, M & Lusk, J (2005) Information theory in wildlife science: critique & viewpoint. J. Wildlife Manage, 69, 457-465.
Guttorp, Peter & Lockhart, Richard A (1988) ”Finding the Location of a Signal: A Bayesian Approach”, Journal of the American Statistical Association 83, 322-330.
Hacking, I (1965) Logic of statistical inference. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Hadley, G (1961) Implicit function theorem – In: Linear Algebra. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company. Boston, Massachusetts, USA.
Haig, S, Della, J, Eagles-Smith, C, Fair, J, Gervais, J, Herring, G, Rivers, J, & Schulz, J (2014) The persistent problem of lead poisoning in birds from ammunition & fishing tackle. The Condor, 116(3): 408-428.
Haldimann, M, A Baumgartner, & B Zimmerli (2002) Intake of Lead from Game Meat—A Risk to Consumers’ Health? European Food Research & Technology 215:375–379.
Hall, S, & F Fisher (1985) Lead Concentrations in Tissues of Marsh Birds & Relationships of Feeding Habits & Grit Preference to Spent Shot Ingestion. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 35:1–8.
Hall, M, J Grantham, R Posey, & A Mee (2007) Lead Exposure Among Reintroduced California Condors in Southern California. In California Condors in the 21st Century (A Mee & L Hall, Editors) Nuttall Ornithological Club, Cambridge, MA, & American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington, DC, USA. Pp. 163–184.
Halley D, Gjershaug J (1998) Inter- & Intra-Specific Dominance Relationships & Feeding Behaviour Of Golden Eagles Aquila Chrysaetos & Sea Eagles Haliaeetus Albicilla At Carcasses. IBIS 140:295–301
Hames, R, Rosenberg, K, Lowe, J, & Dhondt, A (2001) Site reoccupation in fragmented landscapes: testing predictions of metapopulation theory. Journal of Animal Ecology, 70, 182-190.
Hanley, B, & B Dennis (2019) Analytical expressions for the eigenvalues, demographic quantities, & extinction criteria arising from a three-stage wildlife population matrix. Natural Resource Modeling.
Hanley, B., Connelly, P., & Dennis, B. 2019. Another look at the eigenvalues of wildlife population matrix models. PeerJ, 7:e8018 doi.org/10.7717/peerj.8018
Hansen, A, & Hodges, J (1985) High rates of nonbreeding adult Bald Eagles in southeastern Alaska. United States.
Hanspeter, W, & R Kerry (2003) Fall Diet of Chukars (Alectoris Chukar) In Eastern Oregon & Discovery of Ingested Lead Pellets. Western North American Naturalist 63:402– 405.
Harmata A (2011) Environmental Contaminants in Tissues of Bald Eagles Sampled in Southwestern Montana, 2006–2008. Journal of Raptor Research 45:119–135.
Harmata, A, & M Restani (1995) Environmental Contaminants & Cholinesterase in Blood of Vernal Migrant Bald & Golden Eagles in Montana. Intermountain Journal of Sciences 1:1–15.
Harmata, A, & M Restani (2013) Lead, Selenium, & Other Trace Elements in Tissues of Golden Eagles from Southwestern Montana, USA. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 49: 114–124.
Harris, M, Sleeman, J (2007) Morbidity & Mortality of Bald Eagles (Haliaeetus Leucocephalus) & Peregrine Falcons (Falco Peregrinus) Admitted to The Wildlife Center of Virginia, 1993–2003. Journal of Zoo & Wildlife Medicine 38:62–66.
Harris, C (1975) In – Dictionary of Architecture & construction. McGraw Hill Inc. New York, New York, USA.
Hartl, D, & Clark, A (1999) In - Principles of population genetics 4th edition. Sinauer Associates Inc. Publishers. Sunderland, Massachusetts, USA.
Haseltine S, Heinz G, Reichel W, Moore J (1981) Organochlorine & Metal Residues in Eggs of Waterfowl Nesting on Islands in Lake Michigan Off Door County, Wisconsin, 1977–78. Pesticides Monit J 15:90–97.
Hatcher, R (1991) Computer model projections of Bald Eagle nesting in Tennessee. Journal the Tennessee Academy of Science, 66, 225-228.
Hazewinkel, M (ed.) (1988) "Cardano formula" In - Encyclopedia of mathematics. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netherlands.
Hegarty, M, & Kozhevnikov, M (1999) Types of visual-spatial representations & mathematical problem solving. Journal of Educational Psychology, 91, 4, pgs. 684-689.
Heinz, G, D Hoffman, J Klimstra, K Stebbins, S Kondrad, & C Erwin (2009) Species Differences in The Sensitivity of Avian Embryos to Methylmercury. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 56:129–138.
Helander, B, J Axelsson, H Borg, K Holm, & A Bignert (2009) Ingestion of Lead from Ammunition & Lead Concentrations in White-Tailed Sea Eagles (Haliaeetus Albicilla) In Sweden. Science of The Total Environment 407:5555–5563.
Henny C, Blus L, Hoffman D, Grove R (1994) Lead in Hawks, Falcons & Owls Downstream from A Mining Site on The Coeur D’Alene River, Idaho. Environ Monit Assess 29:267–288
Henny, C (2003) Effects of Mining Lead on Birds: A Case History at Coeur d’Alene Basin, Idaho. In Handbook of Ecotoxicology, Second Edition (D. J. Hoffman, B. A. Rattner, G. A. Burton, Jr, & J. Cairns, Jr, Editors) Lewis, Boca Raton, FL, USA. Pp. 755–766.
Heppell, S, Caswell, H, & Crowder, L (2000) Life histories & elasticity patterns: perturbation analysis for species with minimal demographic data. Ecology, 81, 654-665.
Hernández, M, & A Margalida (2008) Pesticide Abuse in Europe: Effects on The Cinereous Vulture (Aegypius Monachus) Population in Spain. Ecotoxicology 17:264–272.
Hernández, M, & A Margalida (2009) Assessing the Risk of Lead Exposure for The Conservation of The Endangered Pyrenean Bearded Vulture (Gypaetus Barbatus) Population. Environmental Research 109:837–842.
Hernández, M (1995) Lead Poisoning in a Free-ranging Imperial Eagle. Supplement to The Journal of Wildlife Diseases 31, Newsletter.
Hernberg, S (2000) Lead Poisoning in a Historical Perspective. American Journal of Industrial Medicine 38:244–254.
Hill H (2009) Taking the Lead on Lead: Tejon Ranch's Experience Switching to Non-Lead Ammunition. In: Watson RT, Fuller M, Pokras M, Hunt WG, Eds. Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans. Boise, ID: The Peregrine Fund; 350. 17.
Hirano, T, I Koike, & C Tsukahara (2004) Lead Shots Retrieved from The Pellets of Eastern Marsh Harriers Wintering in Watarase Marsh, Tochigi Prefecture, Japan. Japanese Journal of Ornithology 53:98–100.
Hodgson, D, & Townley, S (2004) Methodological insight: Linking management changes to population dynamic responses: the transfer function of a projection matrix perturbation. Journal of Applied Ecology, 41:6, 1155-1161.
Hoffman, D, O Pattee, S Wiemeyer, & B Mulhern (1981) Effects of Lead Shot Ingestion On D-Aminolevulinic Acid Dehydratase Activity, Hemoglobin Concentration, & Serum Chemistry in Bald Eagles. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 17:423– 431.
Hoffman, D, J Franson, O Pattee, C Bunck, & H Murray (1985) Biochemical & Hematological Effects of Lead Ingestion in Nestling American Kestrels (Falco Sparverius) Comparative Biochemistry & Physiology C 80:431– 439.
Holladay, J, M Nisanian, S Williams, R Tuckfield, R Kerr, T Jarrett, L Tannenbaum, S Holladay, A Sharma, & R Gogal, Jr (2012) Dosing of Adult Pigeons with As Little as One #9 Lead Pellet Caused Severe D-ALAD Depression, Suggesting Potential Adverse Effects in Wild Populations. Ecotoxicology 21:2331–2337.
Holladay, S, R Kerr, J Holladay, B Meldrum, S Williams, & R Gogal, Jr (2012) Persistent Increase of Blood Lead Level & Suppression Of D-ALAD Activity in Northern Bobwhite Quail Orally Dosed with Even A Single 2-Mm Spent Lead Shot. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 63:421–428.
Hoogland, J (2003) Black-Tailed Prairie Dog (Cynomys Ludovicianus) & Allies. In Wild Mammals of North America: Biology, Management, & Conservation (G Feldhammer, B Thompson, & J Chapman, Editors) Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, MD, USA. Pp. 232–247.
Hooten, M, Garlick, M, & Powell, J (2013) Computational efficient spatial differential equation modeling using homogenization. Journal of Agriculture, Biological, & Environmental Statistics. 18, 3, pgs. 405-428.
Hosmer, D, Lemeshow S (2000) Applied Logistic Regression, 2nd Edn. Wiley, New York
Hough, E (1894) Lead-Poisoned Ducks. For Stream 42:117
Houllier, F, Lebreton, J, & Pontier, D (1989) Sampling properties of the asymptotic behavior of age-or stage-grouped population models. Math Bioscience, 95:2, 161-177.
Houston, D, A Mee, & M Mcgrady (2007) Why Do Condors & Vultures Eat Junk? The Implications For Conservation. Journal of Raptor Research 41: 235–238.
Hoxie, W (1910) Notes on the Bald Eagle in Georgia. Auk, 27, 454.
Hunt W, Burnham W, Parish C, Burnham K, Mutch B, Oaks J (2006) Bullet Fragments in Deer Remains: Implications for Lead Exposure in Avian Scavengers. Wildlife Society Bulletin 34:167–170.
Hunt, W, C Parish, S Farry, T Lord, & R Sieg (2007) Movements of Introduced California Condors in Arizona In Relation to Lead Exposure. In California Condors in the 21st Century (A. Mee & L. S. Hall, Editors) Nuttall Ornithological Club, Cambridge, MA, & American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington, DC, USA. Pp. 79–96.
Hunt, W, Driscoll, D, Mesta, R, Barclay, J, & Jackman, R (2009) Migration & survival of juvenile bald eagles from Arizona. Journal of Raptor Research, 43:2, 121-126.
Hunt, W, Parish, C, Orr, K, & Aguilar, R (2009) Lead poisoning & the reintroduction of the California Condor in Northern Arizona. Journal of Avian Medicine & Surgery, 23(2): 145-150.
Hunt, W, R Watson, J Oaks, C Parish, K Burnham, R Tucker, J Belthoff, & G Hart (2009) Lead Bullet Fragments in Venison from Rifle-Killed Deer: Potential for Human Dietary Exposure. Plos ONE 4(4): E5330.
Hunt, W (2012) Implications of Sublethal Lead Exposure in Avian Scavengers. Journal of Raptor Research 46:389–393.
Hunter, B, Wobeser G (1980) Encephalopathy & Peripheral Neuropathy in Lead-Poisoned Mallard Ducks. Avian Dis 24:169–178 Jacobson E, Carpenter JW, Novilla M (1977) Suspected Lead Toxicosis In A Bald Eagle. JAVMA 171:952–954.
Hunter, B, & M Rosen (1965) Occurrence of Lead Poisoning in A Wild Pheasant (Phasianus Colchicus) California Fish & Game 51:207.
Hurlbert, S, & Lombardi, C (2009) Final collapse of the Neyman-Pearson decision theoretic framework & rise of the neoFisherian. Annales Zoologici Fennici, 46, 311–349.
Hwang, K, B Lee, J Bressler, K Bolla, W Stewart, & B Schwartz (2002) Protein Kinase C Activity & The Relations Between Blood Lead & Neurobehavioral Function in Lead Workers. Environmental Health Perspective 110:133– 138.
International Union for The Conservation of Nature (1998) Guidelines for Reintroductions. Prepared by the IUCN/SSC Reintroduction Specialist Group. IUCN, Gland, Switzerland & Cambridge, UK, 10 Pp.
International Union for The Conservation of Nature (2017) Documentation standards & consistency checks for IUCN Red List assessments & species accounts.
International Union for The Conservation of Nature (2018) Red List Listing criteria. Accessed on 15 February 2019.
Iwata, H, M Watanabe, E Kim, R Gotoh, G Yasunaga, S Tanabe, Y Masuda, & S Fujita (2000) Contamination by Chlorinated Hydrocarbons & Lead in Steller’s Sea Eagle & White-Tailed Sea Eagle from Hokkaido, Japan. Pages 91–106 In M. Ueta & M. Mcgrady (Eds.) First Symposium on Steller’s & White-Tailed Sea Eagles in East Asia. Wild Bird Society of Japan, Tokyo, Japan.
J (Editor) (1978) The Biogeochemistry of Lead in The Environment, Part B: Biological Effects. Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
Jacobson, E, J Carpenter, & M Novilla (1977) Suspected Lead Toxicosis In A Bald Eagle. Journal of The American Veterinary Medical Association 171:952–954.
Janssen, D, J Oosterhuis, J Allen, M Anderson, D Kelts, & S Wiemeyer (1986) Lead Poisoning in Free Ranging California Condors. Journal of The American Veterinary Medical Association 189: 1115–1117.
Jeffreys, H (1961) Theory of Probability, 3rd ed. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1st. ed, 1939)
Johansen, P, G Asmund, & F Riget (2004) High Human Exposure to Lead Through Consumption of Birds Hunted with Lead Shot. Environmental Pollution 127:125–129.
Johnsgard, P (1990) Hawks, Eagles & Falcons of North America. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, DC
Johnsgard, P (1983) Sandhill Crane. Pages 171–184 In Cranes of The World. Croom Helm, London, Canberra.
Johnson, D (1999) The insignificance of statistical significance testing. Journal of Wildlife Management 63:763–772.
Johnson, J & Omland, K (2004) Model selection in ecology & evolution. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 19, 101-108.
Jones, J (1939) On the Occurrence of Lead Shot in Stomachs of North American Gruiformes. Journal of Wildlife Management 3:353–357.
Jones, T, Van Houtan, K, Bostrom, B, Ostafichuk, P, Mikkelson, J, Tezcan, E, Carey, M, Imlach, B, & Seminoff, J (2013) Calculating the ecological impacts of animal-borne instruments on aquatic organisms. Methods in Ecology & Evolution, 4:12, 1178-86.
Judge, G, Griffiths, W, Hill, R, Lutkepohl, H, & Lee, T (1985) The Theory & Practice of Econometrics, Second Edition. Wiley, New York.
Kaiser T, Reichel W, Locke L, Cromartie E, Krynitsky A, Lamont T, Mulhern B, Prouty R, Stafford C, Swineford D (1980) Organochlorine Pesticide, PCB, & PBB Residues & Necropsy Data for Bald Eagles From 29 States: 1975–77.
Kaiser, G, & K Fry (1980) Ingestion of Lead Shot by Dunlin. The Murrelet 61:37.
Kaiser, T, W Reichel, L Locke, E Cromartie, A Krynitsky, T La–Mont, B Mulhern, R Prouty, C Stafford, & D Swineford (1980) Organochlorine Pesticide, PCB, & PBB Residues & Necropsy Data for Bald Eagles From 29 States, 1975–77. Pesticide Monitoring Journal 14:145–149.
Kalisinska, E, W Salicki, & A Jackowski (2006) Six Trace Metals in White-Tailed Eagle from Northwestern Poland. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies 15:727–737.
Kanstrup, N, Swift, J, Stroud, D, & Lewis, M (2018) Hunting with lead ammunition is not sustainable: European perspectives. Ambio.
Katzner, T, Stuber, M, Slabe, V, Anderson, J, Cooper, J, Rhea, L & Milisap, B (2018) Origins of lead in raptors. Animal Conservation, 21:232-240.
Kery, M (2010) Introduction to Winbugs For Ecologists. Academic Press, Burlington
Keel, M, W Davidson, G Doster, & L Lewis (2002) Northern Bobwhite & Lead Shot Deposition in an Upland Habitat. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 43:318–322.
Kelly A, Kelly S (2005) Are Mute Swans with Elevated Blood Lead Levels More Likely to Collide with Overhead Power Lines? Waterbirds 28:331–334.
Kelly, T, & C Johnson (2011) Lead Exposure in Free-Flying Turkey Vultures Is Associated with Big Game Hunting in California. Plos ONE 6(4): E15350.
Kemp, W & Dennis, B (1991) Toward a general model of rangeland grasshopper
Kendall, R., & P Scanlon (1981) Effects of Chronic Lead Ingestion on Reproductive Characteristics of Ringed Turtle Doves (Streptopelia Risoria) & On Tissue Lead Concentrations of Adults & Their Progeny. Environmental Pollution A26:203–213.
Kendall, R, Veit, & P Scanlon (1981) Histological Effects & Lead Concentrations in Tissues of Adult Male Ringed Turtle Doves (Streptopelia Risoria) That Ingested Lead Shot. Journal of Toxicology & Environmental Health 8:649–658.
Kendall, R, T Lacker, Jr, C Bunck, B Daniel, C Driver, C Grue, F Leighton, W Stansley, P Watanabe, & M Whitworth (1996) An Ecological Risk Assessment of Lead Shot Exposure in Non-Waterfowl Avian Species: Upland Game Birds & Raptors. Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry 15:4– 20.
Kennedy, S, J Crisler, E Smith, & M Bush (1977) Lead Poisoning in Sandhill Cranes. Journal of The American Veterinary Medical Association 171:955–958.
Kenntner, N, F Tataruch, & O Krone (2001) Heavy Metals in Soft Tissue of White-Tailed Eagles Found Dead or Moribund in Germany & Austria from 1993 To 2000. Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry 20:1831–1837.
Kenntner, N, O Krone, R Altenkamp, & F Tataruch (2003) Environmental Contaminants in Liver & Kidney of Free-Ranging Northern.
Kenntner, N, F Tataruch, & O Krone (2005) Risk Assessment of Environmental Contaminants. In: White–Tailed Sea Eagles (Haliaeetus Albicilla) From Germany. Pages 125–127 In K. Pohlmeyer (Ed.) Extended Abstracts of The Xxviith Congress of The International Union of Game Biologists, Hannover 2005. DSV Verlag, Hamburg, Germany.
Kenntner, N, Y Crettenand, H Funfstuck, M Janovsky, & F Tataruch (2007) Lead Poisoning & Heavy Metal Exposure of Golden Eagles (Aquila Chrysaetos) From the European Alps. Journal of Ornithology 148:173–177.
Kerr, R, S Holladay, T Jarrett, B Selcer, B Meldrum, S Williams, L Tannenbaum, J Holladay, J Williams, & R Gogal (2010) Lead Pellet Retention Time & Associated Toxicity in Northern Bobwhite Quail (Colinus Virginianus) Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry 29:2869–2874.
Keyfitz, N & Caswell, H (2005) – In: Applied mathematical demography. 3rd Ed. Springer Science. New York, New York, USA.
Keyfitz, N (1964) The population projection as a matrix operator. Demography, 1, 56-73.
Keyfitz, N (1971) On the momentum of population growth. Demography, 8, 71-80.
Keymer, I, & R Stebbings (1987) Lead Poisoning in A Partridge (Perdix Perdix) After Ingestion of Gunshot. Veterinary Records 21: 276–277.
Kim, E, R Goto, H Iwata, S Tanabe, Y Masuda, & S Fujita (1999) Preliminary Survey of Lead Poisoning of Steller’s Sea Eagle (Haliaeetus Pelagicus) & White-Tailed Eagle (Haliaeetus Albicilla) In Hokkaido, Japan. Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry 18:448–451.
Kissel, A, Palen, W, Govindarajulu, P, & Bishop, C (2014) Quantifying ecological life support: The biological efficacy of alternative supplementation strategies for imperiled amphibian populations. Conservation Letters, 7:5, 441-450.
Kliman, R, Sheehy, B, & Schultz, J (2008) Genetic drift & effective population size. Nature Education, 1:3, 3.
Klimko, L, & Nelson, P (1978) On conditional least squares estimation for stochastic processes. The Annals of Statistics, 6, 629-642.
Knight, K (2000) In - Mathematical statistics. Chapman & Hall, Boca Raton, Florida, USA.
Knopper, L, P Mineau, A Scheuhammer, D Bond, & D Mckinnon (2006) Carcasses of Shot Richardson’s Ground Squirrels May Post Lead Hazards to Scavenging Hawks. Journal of Wildlife Management 70:295–299.
Knott, J, J Gilbert, D Hoccom, & R Green (2010) Implications for Wildlife & Humans of Dietary Exposure to Lead from Fragments of Lead Rifle Bullets in Deer Shot in the UK. Science of The Total Environment 409:95–99.
Knott, J, J Gilbert, R Green, & D Hoccom (2009) Comparison of The Lethality of Lead & Copper Bullets in Deer Control Operations to Reduce Lead Poisoning; Field Trials in England & Scotland. Conservation Evidence 6:71–78.
Kochert M, Steenhof K (2002) Golden Eagles in The U.S. & Canada: Status, Trends, & Conservation Challenges. J Raptor Res 36:32–40.
Kochert M, Steenhof K, Mcintyre C, Craig E (2002) Golden Eagle (Aquila Chrysaetos) In: Poole A (Ed) The Birds of North America Online. Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca.
Komdeur, J (1992) Importance of habitat saturation & territory quality for evolution of cooperative breeding in the Seychelles warbler. Nature, 358, 493-495.
Koons, D, Grand, J, Zenner, B, & Rockwell, R (2005) Transient population dynamics: relations to life history & initial population state. Ecological Modeling, 185, 283-297.
Koons, D, Grand, J, & Arnold, J (2006) Population momentum across vertebrate life histories. Ecological Modeling, 197, 418-430.
Koons, D, Rockwell, R, & Grand, J (2006) Population momentum: implications for wildlife management. Journal of Wildlife Management, 70, 19-26.
Koons, D, Holmes, R, & Grand, J (2007) Population inertia & its sensitivity to changes in vital rates & population structure. Ecology, 88, 2857-2867.
Koopman, B (1936) ”On distributions admitting a sufficient statistic”, Trans. Am. Math. Soc, 39, 399-409.
Korte, B, & Vygen J (2018) Combinatorial Optimization: Theory & Algorithms. 6th edition. New York: Springer Publishing.
Kosnett M (2009) Health Effects of Low Dose Lead Exposure in Adults & Children & Preventable Risk Posed by The Consumption of Game Meat Harvested with Lead Ammunition. In: Watson RT, Fuller M, Pokras M, Hunt WG, Eds. Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans. Boise, ID: The Peregrine Fund; 2009:24-33. 21.
Kot, M (2001) An overview of linear age structured models. In - Elements of mathematical ecology. Cambridge University Press. Cambridge, United Kingdom.
Kramer J, Redig P (1997) Sixteen Years of Lead Poisoning in Eagles, 1980–95: An Epizootiologic View. J Raptor Res 31:327–332.
Krone, O, F Wille, N Kenntner, D Boertmann, & F Tataruch (2004) Mortality Factors, Environmental Contaminants, & Parasites of White-Tailed Sea Eagles from Greenland. Avian Diseases 48:417–424.
Kruger, O, Grunkorn, T, Struwe-Juhl, B (2010) The return of the white-tailed eagle (Haliaeetus albicilla) to northern Germany: modelling the past to predict the future. Biological Conservation, 143, 710–721,
Kruschke, J & Vanpaemel, W (2015) Bayesian estimation in hierarchical models. In: J. R. Busemeyer, Z. Wang, J. T. Townsend, & A. Eidels (Eds.), The Oxford Handbook of Computational & Mathematical Psychology, pp. 279-299. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Kuehl, R (2000) In - Design of experiments: Statistical principles of research design & analysis. 2nd Edition. Brooks Cole, Belmont, California, USA.
Kuehler, C, D Sterner, D Jones, R Usnik, & S Kasielke (1991) Report on Captive Hatches of California Condors (Gymnogyps Californianus): 1983–1990. Zoo Biology 10: 65–68.
Kuhl, R (2000) -In: Design of experiments: Statistical principles of research design & analysis, 2nd edition. Brooks Cole, Belmont, California, USA.
Kullback, S & Leibler, R (1951) On information & sufficiency. Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 22, 79-86.
Kurosawa, N (2000) Lead Poisoning in Steller's Sea Eagles & White-Tailed Sea Eagles. Pages 107–109 In M. Ueta & M. J. Mcgrady (Eds.) First Symposium on Steller’s & White-Tailed Sea Eagles in East Asia. Wild Bird Society of Japan, Tokyo, Japan.
Lande, R (1982) A quantitative genetic theory of life history evolution. Ecology, 63:3, 607-615.
Lande, R (1988) Demographic models of the northern spotted owl (Strix occidentalis caurina) Oecologia, 75, 601-607.
Lambertucci, S, J Donazar, A Huertas, B Jimenez, M. Saez, J Sanchez-Zapata, & F Hiraldo (2011) Widening the Problem of Lead Poisoning to A South-American Top Scavenger: Lead Concentrations in Feathers of Wild Andean Condors. Biological Conservation 144:1464–1471.
Langelier, K, C & Ress, T Grey, C Wooldridge, R Lewis, & R Marchetti (1991) Lead Poisoning in Bald Eagles in British Columbia. Canadian Veterinary Journal 32: 108–109.
Larsen, R, J Flinders, D Mitchell, & E Perkins (2007) Grit Size Preferences & Confirmation of Ingested Lead Pellets in Chukars (Alectoris Chukar) Western North American Naturalist 67:152–155.
Lasko T, Bhagwat J, Zou K, Ohno-Machado L (2005) The Use of Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves in Biomedical Informatics. J Biomed Inform 38:404–415.
Lax, P (1997) Positive matrices. - In: Linear algebra. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey, USA.
Lay, D, Lay, S, & MacDonald, J (2016) – In: Linear algebra & its applications. Pearson. London, England.
Lebreton, J et al (1992) Modeling survival & testing biological hypotheses using marked animals: a unified approach with case studies. Ecol. Monogr. 62, 67-118.
Lebreton, J (2005) Age, stages, & the role of generation time in matrix models. Ecological Modelling, 188, 22-29.
Lebreton, J, Nichols, J, Barker, J, Pradel, R, & Spendelow, J (2009) Modeling individual animal histories with multistate capture-recapture models. In - Advances in Ecological Research. Vol. 41. Elsevier. Amsterdam, Netherlands.
Ledoux, D, P Henry, C Ammerman, P Rao, & R Miles (1991) Estimation of The Relative Bioavailability of Inorganic Copper Sources for Chicks Using Tissue Uptake of Copper. Journal of Animal Science 69: 215–222.
Lee, C (2017) Elasticity of population growth with respect to the intensity of biotic or abiotic driving factors. Ecology, 98:4, 1016-1025.
Lefkovitch, L (1965) The study of population growth in organism groups by stages. Biometrics, 21, 1-18.
Leirs, H, Stenseth, N, Nichols, J, Hines, J, Verhagen, R & Verheyen, W (1997) Stochastic seasonality & nonlinear density-dependent factors regulate population size in an African rodent. Nature, 389, 176–180.
Leopold, L (2006) In- A view of the river. Harvard University Press. Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA.
Leslie, P (1945) On the use of matrices in certain population mathematics. Biometrika, 35, 213-245.
Lewis, E (1941) On the generation & growth of a population. Sankhya, Indian Journal of Statistics, 6, 93-96.
Lewis, J, & E Legler (1968) Lead Shot Ingestion by Mourning Doves & Incidence in Soil. Journal of Wildlife Management 32:476– 482.
Lewis, L, R Poppenga, W Davidson, J Fischer, & K Morgan (2001) Lead Toxicosis & Trace Element Levels in Wild Birds & Mammals at a Firearms Training Facility. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 41:208–214.
Lindsay, B (1995) Mixture Models: Theory, Geometry & Applications. NSF-CBMS Regional Conference Series in Probability & Statistics, 5, I-163.
Liu, J, R Goyer, & M Waalkes (2008) Toxic Effects of Metals. In Casarett & Doull’s Toxicology: The Basic Science of Poisons, Seventh Edition (C. D. Klaasen, Editor) Mcgrawhill Medical, New York, NY, USA. Pp. 931–979.
Lly, T, P Bloom, S Torres, Y Hernandez, R Poppenga, W Boyce, & C Johnson (2011) Impact of The California Lead Ammunition Ban on Reducing Lead Exposure in Golden Eagles & Turkey Vultures. Plos ONE 6(4): E17656.
Locke L, Bagley G, Frickie D, Young L (1969) Lead Poisoning & Aspergillosis in an Andean Condor. JAVMA 155:1052–1056
Locke L, Thomas N (1996) Lead Poisoning of Waterfowl & Raptors. In: Fairbrother A, Locke L, Hoff G (Eds) Noninfectious Diseases of Wildlife, 2nd Edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames, Pp 108–117.
Locke, L, & G Bagley (1967) Lead Poisoning in A Sample of Maryland Mourning Doves. Journal of Wildlife Management 31: 515–518.
Locke, L, & M Friend (1992) Lead Poisoning of Avian Species Other Than Waterfowl. Pages 19–22 In D Pain (Ed.) Lead Poisoning in Waterfowl. Proceedings of An IWRB Workshop, Brussels, Belgium, 13–15 June 1991. International Waterfowl & Wetlands Research Bureau Special Publication 16, Slimbridge, UK.
Loehle, C (1987) Hypothesis testing in ecology: psychological aspects & the importance of theory maturation. Quarterly Review of Biology, 62, 397–409.
Lomnicki, A (2011) Individual-based Models in Population Ecology. In: eLS. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Chichester.
Lopez, A (1961) – In: Problems in stable population theory. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey, USA.
Loss, S, T Will, & P Marra (2013) The Impact of Free-ranging Domestic Cats on Wildlife of The United States. Nature Communications 4: Article 1396.
Loss, S, T Will, S Loss, & P Marra (2014) Bird–Building Collisions in The United States: Estimates of Annual Mortality & Species Vulnerability. The Condor 116:8–23.
Lotka, A (1925) Elements of Physical Biology. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, Maryland, USA.
Lucas, J (1982) The biophysics of pit construction by antlion larvae (Myrmeen, Neuroptera) Animal Behaviour, 30, 3, pgs. 651-652.
Lumeiji, J, W Wolvekamp, G Brondietz, & A Schotman (1985) An Unusual Case of Lead Poisoning in A Honey Buzzard (Pernis Apivorus) The Veterinary Quarterly 7:165–168.
Lutmerding, J, & Love, A (2017) Longevity Records of North American Birds. Version 2017.1. Patuxent Wildlife Research Center. Bird Banding Laboratory. Laurel, Maryland.
Muller, Y, L Rivero, M Carvalho, K Kobus, M Farina, & E Nazari (2008) Behavioral Impairments Related to Lead-Induced Developmental Neurotoxicity in Chicks. Archives of Toxicology 82:445–451.
MA, W, Hines J (1994) Effects of Starvation on Muscle & Organ Mass of King Eiders Somateria Spectabilis & The Ecological & Management Implications. Wildfowl 45:188–197
MA, W (2011) Lead in Mammals. In Environmental Contaminants in Biota, W Beyer & J Meador (Eds.) CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, Pp. 595–607.
Macdonald J, Randall C, Ross H, Moon G, Ruthven A (1983) Lead Poisoning in Captive Birds of Prey. Vet Rec 113(3):65–66.
Mallows, C (1972) A Note on Asymptotic Joint Normality. Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 43:2, 508-515.
Mangel, M. & Samaniego, F. J (1984) Abraham Wald's work on aircraft survivability. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 79, 259-267.
Manly, B (2007) – In: Randomization, bootstrap, & Monte Carlo methods in biology. Chapman & Hall. New York, New York, USA.
Mao, J, J Cao, & T Graedel (2009) Losses to The Environment from The Multilevel Cycle of Anthropogenic Lead. Environmental Pollution 157:2670–2677.
Marescot, L, Forrester, T, Casady, D, & Wittmer, H (2014) Using multistate capture–mark–recapture models to quantify effects of predation on age-specific survival &
Marn, C, R Mirachi, & M Lisano (1988) Effects of Diet & Cold Weather on Captive Female Mourning Doves Dosed with Lead Shot. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 17:589–594.
Martin P, Campbell D, Hughes K, Mcdaniel T (2008) Lead in Tissues of Terrestrial Raptors in Southern Ontario, Canada, 1995–2001. Sci Tot Environ 391:96–103.
Martin, G, & J Shaw (2010) Bird Collisions with Power Lines: Failing to See the Way Ahead? Biological Conservation 143: 2695–2702.
Martin, P, & G Barrett (2001) Exposure of Terrestrial Raptors to Environmental Lead: Determining Sources Using Stable Isotope Ratios. Page 84 In International Association for Great Lakes Research Conference Program & Abstracts 44, University of Wisconsin—Green Bay, Green Bay, 10–14 June 2001. IAGLR, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA.
Martin, P, D Campbell, & A Scheuhammer (2003) Lead Exposure in Terrestrial Foraging Raptors in Southern Ontario, 1999–2001. Page 269 In International Association for Great Lakes Research Conference Program & Abstracts 46, Depaul University, Chicago, 22–26 June 2003. IAGLR, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA.
Martin, W (2014) Making valid causal inferences from observational data. Preventative Veterinary Medicine, 13: 281-297.
Martina, P, D Campbell, K Hughes, & T Mcdaniel (2008) Lead in The Tissues of Terrestrial Raptors in Southern Ontario, Canada, 1995–2001. Science of The Total Environment 391: 96–103.
Mateo, R, R Molina, J Grifols, & R Guitart (1997) Lead Poisoning in A Free-ranging Griffon Vulture (Gyps Fulvus) The Veterinary Record 140: 47–48.
Mateo R, Estrada J, Paquet J-Y, Riera X, Domınguez L, Guitart R, Martınez-Vilalta A (1999) Lead Shot Ingestion by Marsh Harriers Circus Aeruginosus From the Ebro Delta, Spain. Environ Pollut 104:435–440.
Mateo, R, R Cadenas, M Manez, & R Guitart (2001) Lead Shot Ingestion in Two Raptor Species from Donana, Spain. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety 48:6–10.
Mateo, R, M Taggart, & A Meharg (2003) Lead & Arsenic in Bones of Birds of Prey from Spain. Environmental Pollution 126:107– 114.
Mateo, R, M Rodriguez-De La Cruz, D Vidal, M. Reglero, & P Camarero (2007) Transfer of Lead from Shot Pellets to Game Meat During Cooking. Science of The Total Environment 372:480–485.
Mateo, R (2009) Lead Poisoning in Wild Birds in Europe & The Regulations Adopted by Different Countries. In Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans (R. T. Watson, M. Fuller, M. Pokras, & W. G. Hunt, Editors) The Peregrine Fund, Boise, ID, USA. Pp. 71–98.
Mateo-Toma ´S, P, & P Olea (2010) Anticipating Knowledge to Inform Species Management: Predicting Spatially Explicit Habitat Suitability of a Colonial Vulture Spreading Its Range. Plos ONE 5(8): E12374.
Matsuda, H (2003) Challenges Posed by The Precautionary Principle & Accountability in Ecological Risk Assessment. Environmetrics 14: 245–254.
Mautino, M, & J Bell (1986) Experimental Lead Toxicity in The Ring-Necked Duck. Environmental Research 41: 538–545.
May, R (1974) - In: Stability & complexity in model ecosystems. 2nd edition. Princeton University Press. Princeton, New Jersey, USA.
Mayo, D, & A Spanos (2006) Severe testing as a basic concept in a Neyman-Pearson philosophy of induction. British Journal for the Philosophy of Science 57:323-357.
Mcbride, T, J Smith, H Gross, & M Hooper (2004) Blood-Lead & ALAD Activity Levels of Cooper’s Hawks (Accipiter Cooperii) Migrating Through the Southern Rocky Mountains. Journal of Raptor Research 38:118–124.
McDonald J, Stott I, Townley S, & Hodgson D (2016) Transients drive the demographics of plant populations in variable environments. Journal of Ecology, 104, 306-314.
McGowan, C, Allan, N, Servoss, J, Hedwall, S, & Wooldridge, B (2017) Incorporating population viability models into species status assessment & listing decisions under the U.S. Endangered Species Act. Global Ecology & Conservation, 12, 119-130.
Mcquirter, J, S Rothenberg, G Dinkins, V Kondrashov, M Manolo, & A Todd (2004) Change in Blood Lead Concentration Up To 1 Year After A Gunshot Wound with A Retained Bullet. American Journal of Epidemiology 159:683–692.
Mee, A, & N Snyder (2007) California Condors in the 21st Century—Conservation Problems & Solutions. In California Condors in the 21st Century, A Mee, L Hall & J Grantham (Eds.) Series in Ornithology, No. 2. American Ornithologists Union, Washington, DC, & Nuttall Ornithological Club, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Pp. 243–279.
Meharg, A, D Pain, R Ellam, R Baos, V Olive, A Joyson, N Powell, A Green, & F Hiraldo (2002) Isotopic Identification of The Sources of Lead Contamination for White Storks (Ciconia Ciconia) In A Marshland Ecosystem (Donana, Spain) Science of The Total Environment 300: 81–86.
Meretsky, V, N Snyder, S Beissin–Ger, D Clendenen, & J Wiley (2000) Demography of The California Condor: Implications for Reestablishment. Conservation Biology 14:957–967.
Mertz, D (1971) The Mathematical Demography of The California Condor Population. American Naturalist 105:437– 453.
Meyer, J, Ingersoll, C, McDonald, L, & Boyce, M, (1986) Estimating uncertainty in population growth rates: jackknife vs. bootstrap techniques. Ecology, 67, 1156-1166.
Meyer, K, & Houle, D (2013) Sampling based approximation of confidence intervals for functions of genetic covariance matrices. 20th Conference of the Association for the Advancement of Animal Breeding & Genetics. Napier, New Zealand.
Migliorini, M, G Pigino, N Bianchi, F Bernini, & C Leonzio (2004) The Effects of Heavy Metal Contamination on The Soil Arthropod Community of a Shooting Range. Environmental Pollution 129:331–340.
Miller, M, M Wayland, E Dzus, & G Bortolotti (2000) Availability & Ingestion of Lead Shotshell Pellets by Migrant Bald Eagles in Saskatchewan. Journal of Raptor Research 34:167–174.
Miller, M. J. R, M. E. Wayland, E. H. Dzus, & G. Bortolotti (2001) Exposure of Migrant Bald Eagles to Lead in Prairie Canada. Environmental Pollution 112:153–162.
Mills, L, & Lindberg, M (2002) Sensitivity analysis to evaluate the consequences of conservation actions. In: S Beissinger, D McCullough (Eds.), Population viability analysis. University of Chicago Press. Chicago, Illinois, USA.
Millsap, B, Harmata, A, Stahlecker, D, & Mikesic, D (2019) Natal Dispersal Distance of Bald & Golden Eagles Originating in the Coterminous United States as Inferred from Band Encounters. Journal of Raptor Research, 48:1, 13-23.
Monte, L (2012) Characterization of a nonlinear Leslie matrix model for predicting the dynamics of biological population in polluted environments: Applications to radioecology. Ecological Modelling, 248, 174-183.
Morishita T, Fullerton A, Lowenstine L, Gardner I, Brooks D (1998) Morbidity & Mortality in Free-Living Raptorial Birds of Northern California: A Retrospective Study, 1983–1994. J Avian Med Surg 12:78–81.
Morris, W & Doak, D (2002) Demographic PVAs: Using projection matrices to assess population growth & viability. – In: Quantitative conservation biology: theory & practice of population viability analysis. Sinauer Associates Inc, Sunderland, Massachusetts, USA.
Mudge, G (1992) Options for Alleviating Lead Poisoning: A Review & Assessment of Alternatives to The Use of Non-Toxic Shot. Pages 23–25 In D.J. Pain (Ed.) Lead Poisoning in Waterfowl. Proceedings of An IWRB Workshop, Brussels, Belgium, 13–15 June 1991. International Waterfowl & Wetlands Research Bureau Special Publication 16, Slimbridge, UK.
Mulhern B, Reichel W, Locke L, Lamont T, Belisle A, Cromartie E, Bagley G, Prouty RM (1970) Organochlorine Residues & Autopsy Data from Bald Eagles 1966-68. Pestic Monit J 4:141–144.
Mulhern, D, Watkins, M, & Sherrod, M (1994) Successful nesting by a pair of Bald Eagles at ages three & four. Journal of Raptor Research, 28:2, 113-114.
Murnane, R, G Meerdink, B Rideout, & M Anderson (1995) Ethylene Glycol Toxicosis In A Captive-Bred Released California Condor (Gymnogyps Californianus) Journal of Zoo & Wildlife Medicine 26: 306–310.
Murtaugh, P (2009) Performance of several variable-selection methods applied to real ecological data. Ecology Letters, 12, 1061-1068.
Murtaugh, P (2014) In defense of P-values. Ecology, 95, 611-617.
Nadjafzadeh M, Hofer H, Krone O (2013) The Link Between Feeding Ecology & Lead Poisoning in White-Tailed Eagles. J Wildl Manag 77:48–57.
National Environmental Policy Act (1970) (42 U.S.C. 4321 et seq. 1969)
National Wildlife Health Laboratory (NWHL) (1985) Lead Poisoning in Non-waterfowl Avian Species. United States Fish & Wildlife Service Unpublished Report.
Nelson, T, Mitchell C, Abbott C (1989) Lead-Shot Ingestion by Bald Eagles in Western Arkansas. Southwest Nat 34:245–249.
Neumann, K (2009) Bald Eagle Lead Poisoning in Winter. In: Watson RT, Fuller M, Pokras M, Hunt WG (Eds) Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans. The Peregrine Fund, Boise, Pp 210–218.
Newth, J, R Cromie, M Brown, R Delahay, A Meharg, C Deacon, G Norton, M O’Brien, & D Pain (2012) Poisoning from Lead Gunshot: Still A Threat to Wild Waterbirds In Britain. European Journal of Wildlife Research 59:195–204.
Nicolson, C, Starfield, A, Kofinas, G, & Kruse, J (2002) Ten heuristics for interdisciplinary modeling projects. Ecosystems, 5:4, 376-384.
Nishii, R (1988) Maximum-likelihood principle & model selection when the true model is unspecified. Journal of Multivariate Analysis 27, 392-403.
Nixon C, Hansen L, Brewer P, Chelsvig J, Esker T, Etter D, Sullivan J, Koerkenmeier R, Mankin P (2001) Survival of White-Tailed Deer in Intensively Farmed Areas of Illinois. Canadian Journal of Zoology 79:581–588.
Noer, H, & J Madsen (1996) Shotgun Pellet Loads & Infliction Rates in Pink-Footed Geese Anser Brachyrhynchus. Wildlife Biology 2:65– 82.
Noon, B & Biles, C (1990) Mathematical demography of spotted owls in the Pacific Northwest. Journal of Wildlife Management, 54, 18-27.
Noon, B & Sauer, J (1992) Population models for passerine birds: structure, parameterization, & analysis. – In: McCullough, D & Barrett, R (eds.), Wildlife 2001: Populations. Elsevier Applied Science. Amsterdam, Netherlands.
Nriagu, Pain, D (1990a) Lead Shot Ingestion by Waterbirds In the Camargue, France: An Investigation of Levels & Interspecific Differences. Environmental Pollution 66:273–285.
O’Connor, A & Sargeant, J (2014) Meta-analysis including data from observational studies. Preventative Veterinary Medicine. Vol. 113, pgs. 313-322.
O’Halloran J, Myers A, Duggan P (1989) Some Sub-Lethal Effects of Lead on Mute Swan Cygnus Olor. J Zool Lond 218:627–632.
Oaks, J, M Gilbert, M Virani, R Watson, C Meteyer, B Rideout, H Shivaprasad, S Ahmed, M Chaudhry, M Arshad, S Mahmood, A Ali, & A Khan (2004) Diclofenac Residues as The Cause of Vulture Decline in Pakistan. Nature 2317 Letters: 1–4.
Oehlert, G (1992) A note on the delta method. The American Statistician. 46,1, pgs. 2729.
Ohlendorf, H, & G Heinz (2011) Selenium in Birds. In Environmental Contaminants. In Biota: Interpreting Tissue Concentrations, Second Edition (W Beyer & J Meador, Editors) CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA. Pp. 669–701.
Okuguchi, K, & Irie, K, (1990) The Schur & Samuelson conditions for a cubic equation. The Manchester School. LVIII:414-418.
Oltrogge, V (2009) Success in Developing Lead-Free, Expanding-Nose Centerfire Bullets. In: Watson RT, Fuller M, Pokras M, Hunt WG, Eds. Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans. Boise, ID: The Peregrine Fund; 2009:310-315. 18.
Ortega, E, Manosa, S, Margalida, A, Sanchez, R, Oria, J. & Gonzalez, L (2009) A demographic description of the recovery of the Vulnerable Spanish imperial eagle Aquila adalberti. Oryx, 43:1, 113-121.
Ott, R (2010) In: An introduction to statistical methods & data analysis. 6th Ed. Brooks & Cole Publishing. Belmont, California, USA.
Pain, D (1990a) Lead Shot Ingestion by Waterbirds In the Camargue, France: An Investigation of Levels & Interspecific Differences. Environmental Pollution 66:273–285.
Pain, D (1990b) Lead Poisoning of Waterfowl: A Review. Pages 172–181 In G. Matthews (Ed.) Managing Waterfowl Populations. The International Waterfowl & Wetlands Research Bureau, Slimbridge, UK.
Pain, D (1991a) Lead Shot Densities & Settlement Rates in Camargue Marshes, France. Biological Conservation 57:273– 286.
Pain, D (1991b) Why Are Lead-Poisoned Waterfowl Rarely Seen? The Disappearance of Waterfowl Carcasses in The Camargue, France. Wildfowl 42:118–122.
Pain, D (1992) Lead Poisoning in Waterfowl: A Review. Pages 7–13 In D.J. Pain (Ed.) Lead Poisoning in Waterfowl. Proceedings of An IWRB Workshop, Brussels, Belgium, 13–15 June 1991. International Waterfowl & Wetlands Research Bureau Special Publication 16, Slimbridge, UK.
Pain D, Amiard-Triquet C (1993) Lead Poisoning of Raptors in France & Elsewhere. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety 25:183–192.
Pain, D, C, Amiard-Triquet, C, Bavoux, G, Burneleau, L, Eon, & P, Nicolauguillaumet (1993) Lead Poisoning in Wild Populations of Marsh Harrier (Circus Aeruginosus) In the Camargue & Charente-Maritime, France. Ibis 135:379–386.
Pain, D, Sears J, Newton I (1995) Lead Concentrations in Birds of Prey in Britain. Environ Pollut 87:173–180.
Pain, D (1996) Lead in Waterfowl. Pages 251– 262 In W. M. Beyer, G. H. Heinz, & A. W. Redman-Norwood (Eds.) Environmental Contaminants in Wildlife: Interpreting Tissue Concentrations. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, Florida, USA.
Pain, D, Bavoux C, Burneleau G (1997) Seasonal Blood Lead Concentrations in Marsh Harriers Circus Aeruginosus From Chatrente-Maritime, France: Relationship with The Hunting Season. Biol Conserv 81:1–7.
Pain, D, A Meharg, M Ferrer, M Taggart, & V Pentariani (2004) Lead Concentrations in Bones & Feathers of The Globally Threatened Spanish Imperial Eagle. Biological Conservation 121:603–610.
Pain, D, I Carter, A Sainsbury, R Shore, P Eden, M Taggart, S Konstantinos, L Walker, A Meharg, & A Raab (2007) Lead Contamination & Associated Disease in Captive & Reintroduced Red Kites Milvus in Engl&. Science of The Total Environment 376:116–127.
Pain, D, Fisher I, Thomas V (2009) A Global Update of Lead Poisoning in Terrestrial Birds from Ammunition Sources. In: Watson RT, Fuller M, Pokras M, Hunt WG (Eds) Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans. The Peregrine Fund, Boise, Pp 99–118.
Parish, C, S Farry, T Lord, & R Seig (2007) Movements of Introduced California Condors in Arizona In Relation to Lead Exposure. In California Condors in the 21st Century, A Mee, L Hall & J Grantham (Eds.) Series in Ornithology, No. 2. American.
Parish, C, W Hunt, E Feltes, R Seig, & K Orr (2009) Lead Exposure Among A Reintroduced Population of California Condors in Northern Arizona & Southern Utah. In Proceedings of The Conference: Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans, R Watson, M Fuller, M Pokras & G Hunt (Eds.) The Peregrine Fund, Boise, Idaho, Pp. 259–264.
Partners in Flight (2017) Avian Conservation Assessment Database. 2017.
Pattee O, Wiemeyer S, Mulhern B, Sileo L, Carpenter J (1981) Experimental Lead-Shot Poisoning in Bald Eagles. Journal of Wildlife Management 45:806–810.
Pattee O, Hennes S (1983) Bald Eagles & Waterfowl: The Lead Shot Connection. Trans N Am Wildl Nat Resour Conf 48:230–237
Pattee, O, P Bloom, J Scott, & M Smith (1990) Lead Hazards Within the Range of The California Condor. The Condor 92: 931–937.
Pattee, O, J Carpenter, S Fritts, B Rattner, S Wiemeyer, J Royle, & M Smith (2006) Lead Poisoning in Captive Andean Condors (Vultur Gryphus) Journal of Wildlife Diseases 42:772–779.
Pauli, J, & S Buskirk (2007) Recreational Shooting of Prairie Dogs: A Portal for Lead Entering Wildlife Food Chains. Journal of Wildlife Management 71:103–108.
Pawitan, Y (2001) In all likelihood: statistical modelling & inference using likelihood. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK.
Picard, N, Chagneau, P, Mortier, F, & Bar-Hen, A (2009) Finding confidence limits on population growth rates: Bootstrap & analytic methods. Mathematical Biosciences, 219, 23-31.
Pickett, S, & White, P (1985) In- The ecology of natural disturbance & patch dynamics. Academic Press. Orlando, Florida, USA.
Pike, D, Pizzatto, L, Pike, B, & Shine, R (2008) Estimating survival rates of uncatchable animals: the myth of high juvenile mortality in reptiles. Ecology, 89:3, 607-611.
Pinero, D, Martínez-Ramos, M, & Sarukhan, J (1984) A Population model of Astrocaryum mexicanum & a sensitivity analysis of its finite rate of increase. Journal of Ecology, 72, 3, pgs. 977-991.
Platt, J (1976) Bald Eagles Wintering in The Utah Desert. American Birds 30: 783–788.
Pokras, M, & R Chafel (1992) Lead Toxicosis From Ingested Fishing Sinkers in Adult Common Loons (Gavia Immer) In New England. Journal of Zoo & Wildlife Medicine 23:92–97.
Pokras, M, M Kneel &, A Major, R Miconi, & R Poppenga (2009) Lead Objects Ingested by Common Loons in New England. In Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans (R Watson, M Fuller, M Pokras, & W Hunt, Editors) The Peregrine Fund, Boise, ID, USA. Pp. 283–287.
Potts, G (2005) Incidence of Ingested Lead Gunshot in Wild Grey Partridges (Perdix Perdix) From The UK. European Journal of Wildlife Research 51:31–34.
Puls, R (1994) Mineral Levels in Animal Health. Sherpa International, Clearbrook, Canada, Pp. 294–296.
Puschner, B, J St. Leger, & F Galey (1999) Normal & Toxic Zinc Concentrations in Serum/ Plasma & Liver of Psittacines With Respect to Genus Differences. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation 11: 522–527.
Quinn, J & Dunham, A (1983) On hypothesis testing in ecology & evolution. Am. Nat. 122, 602-617.
Quortrup, E, & J Shillinger (1941) 3,000 Wild Bird Autopsies on Western Lake Areas.
R Core Team (2019) R: A language & environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. R version 3.5.3 (2019-03-11)
R Shiny (2018) Shiny. Web Application Framework for R. [Accessed 12 Oct 2018]
Radomski, P, T Heinrich, T Jones, P Rivers, & P Talmage (2006) Estimates of Tackle Loss for Five Minnesota Walleye Fisheries. North American Journal of Fisheries Management 26:206–212.
Ramey, Rr. & R Sibley (1986) Nestsite Biology of The California Condor. Condor 88: 228–241.
Rattner B, Franson J, Sheffield S, (2008) Sources & Implications of Lead Ammunition & Fishing Tackle to Natural Resources. The Wildlife Society Technical Review. Bethesda, MD: The Wildlife Society, 8, 3.
Rattner, B, J Franson, S Sheffield, C Goddard, N Leonard, D Stang, & P Wingate (2008) Sources & Implications of Lead Ammunition & Fishing Tackle on Natural Resources. Technical Review 08-01. The Wildlife Society & American Fisheries Society, Bethesda, MD, USA.
Redig, P (1979) Lead Poisoning in Raptors. Hawk Chalk 18:29–30. Redig PT, Arent LR (2008) Raptor Toxicology. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Exotic Animal Practice 11(2):261–282.
Redig, P, C Stowe, D Barnes, & T Arent (1980) Lead Toxicosis In Raptors. Journal of The American Veterinary Association 177:941–943.
Redig, P, E Lawler, S Schwartz, J Dunnette, B Stephenson, & G Duke (1991) Effects of Chronic Exposure to Sub-Lethal Concentrations of Lead Acetate on Heme Synthesis & Immune Function in Red-Tailed Hawks. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 21:72–77.
Redig, P, Smith, D, Cruz-Martinez, L (2009) Potential Sources of Lead Exposure: A Retrospective Study. Pages 208–209 In Watson RT, Fuller M, Pokras M, Hunt WG, Editors. Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans. Boise, Idaho: The Peregrine Fund.
Reeve, A, & T Vosburgh (2005) Recreational Shooting of Prairie Dogs. In Conservation of The Black-Tailed Prairie Dog (J. L. Hoogland, Editor) Island Press, Washington, DC, USA. Pp. 139–156.
Regehr, E, Hunter, C, Caswell, H, Amstrup, S & Stirling, I (2010) Survival & breeding of polar bears in the southern Beauford Sea in relation to sea ice. Journal of Animal Ecology, 79, 117-127.
Reichel W, Schmeling S, Cromartie E, Kaiser T, Krynitsky A, Lamont T, Mulhern B, Prouty R, Stafford C, Swineford D (1984) Pesticide, PCB, & Lead Residues & Necropsy Data for Bald Eagles From 32 States: 1978-81. Environ Monit Assess 4:395–403.
Reiser, M, & S Temple (1981) Effect of Chronic Lead Ingestion on Birds of Prey. Pages 21–25 In J. E. Cooper & A. G. Greenwood (Eds.) Recent Advances in The Study of Raptor Diseases. Chiron Publications, Keighley, UK.
Rencher, A (2002) -In: Methods of multivariate analysis. John Wiley & Sons Inc. New York, New York, USA.
Renshaw, E (1994) Chaos in biometry. IMA Journal of Mathematics Applied in Medicine & Biology, 1, 17-44.
Rice, J (2007) Mathematical Statistics & Data Analysis, Third Edition. Brooks/Cole, Belmont, California.
Richards, S (2005) Testing ecological theory using the information-theoretic approach: examples & cautionary results. Ecology, 86, 2805–2814.
Richards, S. A (2005) Testing ecological theory using the information-theoretic approach: examples & cautionary results. Ecology, 86, 2805–2814.
Rideout, B, I Stalis, R Papendick, A Pessier, B Puschner, M Finkelstein, D Smith, M Johnson, M Mace, R Stroud, J Brandt, J Burnett, Et Al (2012) Patterns of Mortality in Free-ranging California Condors (Gymnogyps Californianus) Journal of Wildlife Diseases 48:95–112.
Rideout, J Hamber, J Todd, G Austin, M Clark, & M Wallace (2007) Junk Ingestion & Nestling Mortality in A Reintroduced Population of California Condors Gymnogyps Californianus. Bird Conservation International 17: 119–130.
Riley, T, & J Schulz (2001) Predation & Ring-Necked Pheasant Population Dynamics. Wildlife Society Bulletin 29: 33–38.
Rocke T, Samuel M (1991) Effects of Lead Shot Ingestion on Selected Cells of The Mallard Immune System. J Wildl Dis 27:1–9.
Rodrigue, J, R Mcnicoll, D Leclair, & J Duchesne (2005) Lead Concentrations in Ruffed Grouse, Rock Ptarmigan, & Willow Ptarmigan in Quebec. Archives of Environ– Mental Contamination & Toxicology 49:97– 104.
Rodriguez-Ramos Fernandez J, Hofle U, Mateo R, De Francisco O, Abbott R, Acevedo P, Blanco J (2011) Assessment of Lead Exposure in Spanish Imperial Eagle (Aquila Adalberti) From Spent Ammunition in Central Spain. Ecotoxicology 20:670–681.
Rodriguez-Ramos, J, V Gutierrez, U Hofle, R Mateo, L Monsalve, E Crespo, J Blanco (2009) Lead in Griffon & Cinereous Vultures in Central Spain: Correlations Between Clinical Signs & Blood Lead Levels. Extended Abstract in R Watson, M Fuller, M Pokras, & W Hunt (Eds.) Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans. The Peregrine Fund, Boise, Idaho, USA.
Rogers, A (1966) The multiregional matrix growth operator & the stable interregional age structure. Demography, 3, 537-544.
Ross-Winslow, D, & T Teel (2011) The Quest to Eliminate Lead from Units of The National Park System: Understanding & Reaching Out to Audiences. The George Wright Forum 28: 34–77.
Route, W, Key R, Russell R, Lindstrom A, Strynar M (2014) Spatial & Temporal Patterns in Concentrations of Perfluorinated Compounds in Bald Eagle Nestlings in the Upper Midwestern United States. Environ Sci Technol.
Royall, R (1997) Statistical Evidence: A Likelihood Paradigm. Chapman & Hall, London.
Royall, R (2000) On the probability of observing misleading statistical evidence, with commentary. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 95, 760-780.
Royama, T (1992) In - Analytical Population Dynamics. Chapman, Hall, London, United Kingdom.
RStudio Team (2015) RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio, Inc, Boston, MA [Accessed 12 Oct 2018]
Russell R, Franson J (2014) Causes of Mortality in Eagles Submitted to the National Wildlife Health Center 1975–2013. Wildlife Society Bulletin 38(4):697– 704.
Ruxton, G, & D Houston (2004) Obligate Vertebrate Scavengers Must Be Large Soaring Fliers. Journal of Theoretical Biology 228:431–436.
Sanders, T, Liu, V Buchner, & P Tchounwou (2009) Neurotoxic Effects & Biomarkers of Lead Exposure: A Review. Reviews on Environmental Health 24:15–45.
Sanderson, G, & F BELLROSE (1986) A Review of The Problem of Lead Poisoning in Waterfowl. Illinois Natural History Survey, Special Publication 4:1–34.
Sabine, N, Klimstra WD (1985) Ecology of Bald Eagles Wintering in Southern Illinois. Trans Ill Acad Sci 78:13–24.
Saether, B, Tufto, J, Engen, S, Jerstad, K, Rostad, O, & Skatan, J (2000) Population dynamical consequences of climate change for a small temperate songbird. Science, 287, 854–856.
Saether, B, Sutherland, W, & Engen, S (2004) Climate influences on avian population dynamics. Advances in Ecological Research, 35, 185–209.
Sainsbury, A, P Bennett, & J Kirkwood (1995) The Welfare of Free-Living Wild Animals in Europe: Harm Caused by Human Activities. Animal Welfare 4:183–206.
Saito, K (2009) Lead Poisoning of Steller’s Sea-Eagle (Haliaeetus Pelagicus) & White-Tailed Eagle (Haliaeetus Albicilla) Caused by The Ingestion of Lead Bullets & Slugs, In Hokkaido Japan. In Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans (R Watson, M Fuller, M Pokras, & W Hunt, Editors) The Peregrine Fund, Boise, ID, USA. Pp. 302–309.
Sakamoto, Y, M Ishiguru, & G Kitagawa (1986) Akaike Information Criteria Statistics. D. Reidel, New York.
Salguero-Gomez R, Jones O, Archer C, Buckley Y, Che-Castaldo J, Caswell H, Hodgson D, Scheuerlein A, Conde D, Brinks E, de Buhr H, Farack C, Gottschalk F, Hartmann A, Henning A, Hoppe G, Romer G, Runge J, Ruoff T, Wille J, Zeh S, Davison R, Vieregg D, Baudisch A, Altwegg R, Colchero F, Dong M, de Kroon H, Lebreton J, Metcalf C, Neel M, Parker I, Takada T, Valverde T, Velez-Espino LA, Wardle G, Franco M, Vaupel J (2014) The COMPADRE plant matrix database: an open online repository for plant demography. Journal of Ecology, 103(1), pgs 202-218.
Salguero-Gomez R, Jones O, Archer C, Bein C, de Buhr H, Farack C, Gottschalk F, Hartmann A, Henning A, Hoppe G, Romer G, Ruoff T, Sommer V, Wille J, Voigt J, Zeh S, Vieregg D, Buckley Y, Che-Castaldo J, Hodgson D, Scheuerlein A, Caswell H, Vaupel J, & Coulson T (2016) COMADRE: a global data base of animal demography, Journal of Animal Ecology, 85(2), 371.
Saltelli, A, Tarantola, S, Campolongo, F, & Ratto, M (2004) In - Sensitivity analysis in practice: A guide to assessing scientific models. John Wiley & Sons. Hoboken, New Jersey, USA.
Samaniego, F (2014) Stochastic Modeling & Mathematical Statistics: A Text for Statisticians & Quantitative Scientists. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Samour, J, Naldo J (2002) Diagnosis & Therapeutic Management of Lead Toxicosis in Falcons in Saudi Arabia. Journal of Avian Medicine & Surgery 16:16– 20.
Samuel, M, & E Bowers (2000) Lead Exposure in American Black Ducks After Implementation of Non-Toxic Shot. Journal of Wildlife Management 64:947–953.
Samuelson, P (1941) Conditions that the roots of a polynomial be less than unity in absolute value. Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 12, 360-364.
Sauer, J, D Niven, J Hines, D Ziolkowski, Jr, K Pardieck, J Fallon, & W Link (2017) The North American Breeding Bird Survey, Results & Analysis 1966–2015. Version 2.07.2017. USGS Patuxent Wildlife Research Center, Laurel, MD, USA.
Schaub, M, Abadi, F (2011) Integrated population models: a novel analysis framework for deeper insights into population dynamics. Journal of Ornithology, 152: S2:27-S2:37.
Schaub, M & Fletcher, D (2015) Estimating immigration using a Bayesian integrated population model: choice of parametrization & priors. Environ Ecol Stat, 22: 535-549.
Scheaffer, R, Mendenhall II, W, & Ott, R (2006) In - Elementary survey sampling. 6th Ed. Thomson, Brooks & Cole. Belmont, California, USA.
Scheuhammer, A (1987) The Chronic Toxicity of Aluminium, Cadmium, Mercury, & Lead in Birds: A Review. Environmental Pollution 46: 263–295.
Scheuhammer, A, & S Norris (1995) A Review of The Environmental Impacts of Lead Shotshell Ammunition & Lead Fishing Weights in Canada. Occasional Paper 88. Of the Canadian Wildlife Service, Ottawa, Ontario.
Scheuhammer, A, & S Norris (1996) The Ecotoxicology of Lead Shot & Lead Fishing Weights. Ecotoxicology 5:279–295.
Scheuhammer, A, J Perrault, E Routhier, B Braune, & G Campbell (1998) Elevated Lead Concentrations in Edible Portions of Game Birds Harvested with Lead Shot. Environmental Pollution 102:251–257.
Scheuhammer, A, C Rogers, & D Bond (1999) Elevated Lead Exposure in American Woodcock (Scolopax Minor) In Eastern Canada. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 36:334–340.
Scheuhammer, A, D Bond, N Burgess, & J Rodriguez (2003) Lead & Stable Lead Isotope Ratios in Soil, Earthworms, & Bones of American Woodcock (Scolopax Minor) From Eastern Canada. Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry 22:2585–2591.
Schroeder, S, D Fulton, W Penning, & K Doncarlos (2012) Using Persuasive Messages to Encourage Hunters to Support Regulation of Lead Shot. Journal of Wildlife Management 76:1528–1539.
Schmutz, J, K Rose, & R Johnson (1989) Hazards to Raptors from Strychnine Poisoned Ground Squirrels. Journal of Raptor Research 23:147–151.
Schulz, J, J Millspaugh, B Washburn, G Wester, J Lanigan III, & J Franson (2002) Spent-Shot Availability & Ingestion on Areas Managed for Mourning Doves. Wildlife Society Bulletin 30:112–120.
Schulz, J, J Millspaugh, D Zekor, & B Washburn (2003) Enhancing Sport Hunting Opportunities for Urbanites. Wildlife Society Bulletin 31:565–573.
Schulz, J, J Millspaugh, A Bermudez, X Gao, T Bonnot, L Britt, & M Paine (2006) Acute Lead Toxicosis In Mourning Doves. Journal of Wildlife Management 70:413– 421.
Schulz, J, P Padding, & J Millspaugh (2006) Will Mourning Dove Crippling Rates Increase with Nontoxic-Shot Regulations? Wildlife Society Bulletin 34:861–865.
Schulz, J, X Gao, J Millspaugh, & A Bermudez (2007) Experimental Lead Pellet Ingestion in Mourning Doves (Zenaida Macroura) American Midland Naturalist 158:177– 190.
Scott, J. M (ed.) 2006. In - The Endangered Species Act at thirty: Conserving biodiversity in human-dominated landscapes. Island Press. Washington D. C, USA.
Schulz, J, J Fleming, & S Gao (2012) 2011 Mourning Dove Harvest Monitoring Program Annual Report. Missouri Department of Conservation, Resource Science Division, Columbia, MO, USA.
Seamans, M, R Rau, & T Sanders (2012) Mourning Dove Population Status, U.S. Department of The Interior, Fish & Wildlife Service, Division of Migratory Bird Management, Washington, DC, USA.
Sears, J (1988) Regional & Seasonal Variations in Lead Poisoning in The Mute Swan Cygnus Olor In Relation to The Distribution of Lead & Lead Weights, in the Thames Area, England. Biological Conservation 46:115–134.
Seber, G (1984) - In: Multivariate observations. John Wiley & Sons. New York, New York, USA.
Sergeyev, A, & N Shulyatieva (2005) Meat Quality of Birds After Using Lead Shot. Pages 472–473 In K. Pohlmeyer (Ed.) Ex– Tended Abstracts of The Xxviith Congress of The International Union of Game Biologists, Hannover 2005. DSV Verlag, Hamburg, Germany.
Severini,T (2000) Likelihood Methods in Statistics. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK.
Sharley, A, L Best, J Lane, & P Whitehead (1992) An Overview of Lead Poisoning in Australian Waterfowl & Implications for Management. Pages 73–77 In D Pain (Ed.) Lead Poisoning in Waterfowl. Proceedings of An IWRB Workshop, Brussels, Belgium, 13–15 June 1991. International Waterfowl & Wetlands Research Bureau Special Publication 16, Slimbridge, UK.
Shea, K, & Kelly, D (1998) Estimating biocontrol agent impact with matrix models: Catrduuts nutans in New Zealand. Ecological Applications, 8, 824-832.
Sherrod, S, White, C. & Williamson, F (1976) Biology of the Bald Eagle on Amchitka Island, Alaska. Living Bird, 15, 143-182.
Shyu, E, & Caswell, H (2014) Calculating second derivatives of population growth rates for ecology & evolution. Methods in Ecology & Evolution, 5, 473-482.
Sibley, D (2014) The Sibley guide to birds, second edition. Alfred A. Knopf, New York, USA.
Sibly, R, Hansen, F & Forbes, V (2000) Confidence intervals for population growth rate of organisms with two-stage life histories. Oikos, 88, 335-340.
Sieg, R, K Sullivan, & C Parish (2009) Voluntary Lead Reduction Efforts Within the Northern Arizona Range of The California Condor. In Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans (R Watson, M Fuller, M Pokras, & W Hunt, Editors) The Peregrine Fund, Boise, ID, USA. Pp. 341–349.
Sileo, L, & S Fefer (1987) Paint Chip Poisoning of Laysan Albatross at Midway Atoll. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 23:432–437.
Sileo, L, L Creekmore, D Audet, M Snyder, C Meteyer, J Franson, L Locke, M Smith, & D Finley (2001) Lead Poisoning of Waterfowl by Contaminated Sediment in The Coeur d'Alene River. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology, 41:364–368.
Silvertown, J, & Franco, M (1989) COMPADRE: Plant Matrix Database. Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research.
Silvertown, J, Franco, M, & Menges, E (1996) Interpretation of elasticity matrices as an aid to the management of plant populations for conservation. Conservation Biology, 10, 591-597.
Simons, T (1993) Lead–Calcium Interactions in Cellular Lead Toxicity. Neurotoxicology 14:77–85.
Skalski, J, Millspaugh, J, Dillingham, P & Buchanan, R (2007) Calculating the variance of the finite rate of population change from a matrix model in Mathematica. Environmental Modelling & Software, 22, 359-364.
Smith, G, Murillo-Garcia, O, Hostetler, J, Mearns, R, Rollie, C, Newton, I, McGrady, M, & Oli, M (2015) Demography of population recovery: survival & fidelity of peregrine falcons at various stages of population recovery. Oecologia, 178, 391-401.
Smith J, Farmer C, Hoffman S, Kaltenecker G, Woodruff K, Sherrington P (2008) Trends in Autumn Counts of Migratory Raptors in Western North America. In: Bildstein KL, Smith JP, Ruelas Inzunza E, Veit RR (Eds) State of North America’s Birds of Prey. Series in Ornithology 3. Nuttall Ornithological Club, Cambridge & American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington DC, Pp. 217–251.
Smith, M, M Davison, C Schexnider, L Wilson, J Bohannon, J Grassley, D Kraege, W S. Boyd, B Smith, M Jordan, & C Grue (2009) Lead Shot Poisoning in Swans: Sources of Pellets Within Whatcom County, WA, USA, & Sumas Prairie, BC, Canada. In Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans (R Watson, M Fuller, M Pokras, & W Hunt, Editors) The Peregrine Fund, Boise, ID, USA. Pp. 274–277.
Snyder, N, H Snyder, J Lincer, & R Reynolds (1973) Organochlorines, Heavy Metals & The Biology of North American Accipiters. Biosciences 23:300–305.
Snyder, N, & H Snyder (1989) Biology & Conservation of The California Condor. Current Ornithology 6:175–267.
Snyder, N, & H, Snyder (2000) The California Condor: A Saga of Natural History & Conservation. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, USA.
Sorvari, J, R Antikainen, & O Pyy (2006) Environmental Contamination at Finnish Shooting Ranges—The Scope of The Problem & Management Options. Science of The Total Environment 366:21–31.
Southwest Condor Review Team (2012) A Review of The Third Five Years of the California Condor Reintroduction Program in The Southwest (2007–2011) Prepared for The USFWS Arizona Ecological Services Office, Phoenix, AZ, USA.
Spanos, A (2010) Akaike-type criteria & the reliability of inference: Model selection versus statistical model specification. Journal of Econometrics 158:204-220.
Stahl, J, & Oli, M (2006) Relative importance of avian life-history variables to population growth rate. Ecological Modelling, 198, 22–39,
Stansley, W, & D Roscoe (1996) The Uptake & Effects of Lead In Small Mammals & Frogs at a Trap & skeet Range. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 30: 220–226.
Stansley, W, & Murphy, L (2011) Liver lead concentrations in raptors in New Jersey, USA, 2008-2010. Bull. Enviro. Contam. Toxicol. 87:171-174.
Starfield, A, & Bleloch, A (1986) Building models for conservation & wildlife management – MacMillan. South Dakota State University, Brookings, SD, USA.
Starfield, A (1997) A pragmatic approach to modeling for wildlife management. Journal of Wildlife Management, 61:2, 261-270.
Stauber, E, N Finch, P Talcott, & J Gay (2010) Lead Poisoning of Bald (Haliaeetus Leucocephalus) & Golden (Aquila Chrysaetos) Eagles in The U.S. Inland Pacific Northwest Region—An 18-Year Retrospective Study: 1991–2008. Journal of Avian Medicine & Surgery 24:279–287.
Stendell, R, R Smith, K Burnham, & R Christensen (1979) Exposure of Waterfowl to Lead: A Nationwide Survey Of Residues In Wing Bones of Seven Species, 1972–1973. U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Special Scientific Report Wildlife 223:1–12.
Stendell, R (1980) Dietary Exposure of Kestrels to Lead. Journal of Wildlife Management 44:527–530.
Stendell, R, J Artmann, & E Martin (1980) Lead Residues in Sora Rails from Maryland. Journal of Wildlife Management 44:525– 527.
Stenseth, N, Viljugrein, H, Saitoh, T, Hansen, T, Kittilsen, M, Bolviken, E. et al (2003) Seasonality, density dependence, & population cycles in Hokkaido voles. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 100, 11478–11483.
Stephens, P, Buskirk, S, Hayward, G, & Martinez del Rio, C (2005) Information theory & hypothesis testing: a call for pluralism. J. Applied Ecol, 42, 4-12.
Stevenson, A, A Scheuhammer, & H Chan (2005) Effects of Nontoxic Shot Regulations on Lead Accumulation in Ducks & American Woodcock in Canada. Archives of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 48:405–413.
Stoddard, H (1931) The Bobwhite Quail, Its Habits, Preservation & Increase. Charles Scribner’s Sons, New York, USA.
Stone, W, & S Butkas (1978) Lead Poisoning in A Wild Turkey. New York Fish & Game Journal 25:169. SZYMCZAK, M. R. 1978. Steel Shot Use on A Goose Hunting Area in Canada. Wildlife Society Bulletin 6:217–225.
Stott, I, Franco, M, Carslake, D, Townley, S, & Hodgson, D (2010) Boom or bust? A comparative analysis of transient population dynamics in plants. Journal of Ecology, 98:2, 302-311.
Stott, I, Townley, S, & Hodgson, D (2011) A framework for studying transient dynamics of population projection matrix models. Ecology Letters, 14, 959-970.
Stott, I, Hodgson, D, & Townley, S (2012) Popdemo: An R package for population demography using projection matrix analysis. Methods in Ecology & Evolution, 3, 797-802.
Stott, I (2016) Perturbation analysis of transient population dynamics using matrix projection models. Methods in Ecology & Evolution, 7, 666-678.
Strom, S, J Langenberg, N Businga, & J Batten (2009) Lead Exposure in Wisconsin Birds. In Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications For Wildlife & Humans (R Watson, M Fuller, M Pokras, & W Hunt, Editors) The Peregrine Fund, Boise, ID, USA. Pp. 194–201.
Strong, D (1980) Null hypotheses in ecology. Synthese, 43, 271–285.
Strong, D, A Whipple, A Child, L, & Dennis, B (1999) Model selection for a subterranean trophic cascade: root-feeding caterpillars & entomopathogenic nematodes. Ecology, 80, 2750-2761.
Stuart, A, & Ord, K (1998) In - Kendall’s Advanced Theory of Statistics. 6th Edition, Volume 1, Wiley. London, United Kingdom.
Sturtz, S, Ligges, U, Gelman, A (2005) R2winbugs: A Package for Running Winbugs From R. J Stat Software 12:1–16
Sullivan, B, C Wood, M Iliff, R Bonney, D Fink, & S Kelling (2009) eBird: a citizen-based bird observation network in the biological sciences. Biological Conservation 142: 2282-2292.
Sullivan, K, R Sieg, & C Parish (2007) Arizona’s Efforts to Reduce Lead Exposure in California Condors. In California Condors in the 21st Century (A. Mee & L. S. Hall, Editors) Nuttall Ornithological Club, Cambridge, MA, & American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington, DC, USA. Pp. 109–121.
Swenson, J, Alt, K, Eng, R (1986) In - Ecology of Bald Eagles in the greater Yellowstone ecosystem, 1st edition. The Wildlife Society, Bethesda, MD, USA.
Symonds, M & Moussalli, A (2011) A brief guide to model selection, multimodel inference & model averaging in behavioural ecology using Akaike's information criterion. Behav Ecol Sociobiol, 65, 13–21.
Takeuchi, K (1976) Distribution of informational statistics & a criterion for model fitting. Suri-Kagaku (Mathematical Sciences) 153:12-18 (In Japanese)
Taper, M & S Lele eds (2004) The nature of scientific evidence: statistical, philosophical & empirical considerations. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Taper, M, & J Ponciano (2016) Evidential statistics as a statistical modern synthesis to support 21st century science. Population Ecology 58:9-29.
Tavernier, P, S Roels, K Baert, K Hermans, F Pasmans, & K Chiers (2004) Lead Intoxication by Ingestion of Lead Shot in Racing Pigeons (Columba Livia) Vlaams Diergeneeskundig Tijdschrift 73:307–309.
Thomas, C, J Mensik, & C Feldheim (2001) Effects of Tillage on Lead Shot Distribution in Wetland Sediments. Journal of Wildlife Management 65:40–46.
Thomas, V, & R Guitart (2005) Role of International Conventions in Promoting Avian Conservation Through Reduced Lead Toxicosis: Progression Towards A Non-Toxic Agenda. Bird Conservation International 15:147–160.
Thomas, V (1997) The Environmental & Ethical Implications of Lead Shot Contamination of Rural Lands in North America. Journal of Agricultural & Environmental Ethics 10:41–54.
Thomas, V (2009) The Policy & Legislative Dimensions of Nontoxic Shot & Bullet Use in North America. In Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans (R Watson, M Fuller, M Pokras, & W Hunt, Editors) The Peregrine Fund, Boise, ID, USA. Pp. 351–362.
Thomas, V (2010). Achieving Uniform Regulation of Environmental Lead Exposure & Poisoning in Wildlife & Humans. Environmentalist 30: 206– 210.
Thomas, V (2011) Conflicts in Lead Ammunition & Sinker Regulation: Considerations for U.S. National Parks. The George Wright Forum 28:24–33.
Thomas, V (2013) Lead-Free Hunting Rifle Ammunition: Product Availability, Price, Effectiveness, & Role in Global Wildlife Conservation. AMBIO 42:737–745.
Thurmond Mc, & Y Choi (2004b) Influence of Age & Production Type on Liver Copper Concentrations in Calves. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation 16: 382–387.
Tong, H (1990) -In: Nonlinear time series: a dynamical systems approach. Oxford University Press, London, United Kingdom.
Townley, S, & Hodgson, D (2008) Erratum et addendum: transient amplification & attenuation in stage-structured population dynamics. Journal of Applied Ecology, 45:6, 1836-1839.
Tranel, M, Kimmel, R (2009) Impacts of Lead Ammunition on Wildlife, The Environment, & Human Health—A Literature Review & Implications for Minnesota. Pages 318–337 In Watson RT, Fuller M, Pokras M, Hunt WG, Editors. Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications For Wildlife & Humans. Boise, Idaho: The Peregrine Fund.
Trinogga, A, G Fritsch, H Hofer, & O Krone (2012) Are Leadfree Hunting Rifle Bullets as Effective at Killing Wildlife as Conventional Lead Bullets? A Comparison Based on Wound Size & Morphology. Science of The Total Environment 443: 226–232.
Trust, K, Miller, M, Ringelman, J, Orme I (1990) Effects of Ingested Lead on Antibody Production in Mallards (Anas Platyrhynchos) J Wildl Dis 26:316–322.
Tsuji, L, E Nieboer, J Karagatzides, R Hanning, & B Katapatuk (1999) Lead Shot Contamination in Edible Portions of Game Birds & Its Dietary Implications. Ecosystem Health 5:183–192.
Tuljapurkar, S (1989) An uncertain life: demography in random environments. Theoretical Population Biology, 35, 227-294.
Tuljapurkar, S (1990) Population dynamics in variable environments. Lecture notes in Biomathematics Vol. 85. Springer, New York, New York, USA.
Tuljapurkar, S (1994) Stochastic demography & life histories. In - Frontiers in Mathematical Biology, S.A. Levin (ed.), Springer Verlag, 254-262.
Tuljapurkar, S (1997) Demographic uncertainty & the stable equivalent population. Mathematical Computational Modeling, 26, 39-56.
Tuljapurkar, S (2002) Population Biology. In - Encyclopedia of Population, Paul Demeny & Geoff McNicol (Eds.), Macmillan, New York, New York, USA.
Tuljapurkar, S (2003) The Emergence of Modern Human Mortality Patterns. In: The Evolution of Population Biology - Modern Synthesis. Editors: Rama Singh, Marcy Uyenoyama, & Subodh Jain. Cambridge University Press.
Tuljapurkar, S (2008) Stable population theory. In - The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics. 2nd Edition (eds) Steven N. Durlauf & Lawrence E. Blume. Palgrave Macmillan, London, United Kingdom.
Turchin, P (1995) Population regulation: old arguments & a new synthesis. In: Population Dynamics: new approaches & synthesis (eds Cappucino, N. & Price, P.W.) Academic Press San Diego, California, USA.
Ueta, M, & V Masterov (2000) Estimation by A Computer Simulation of Population Trend of Steller’s Sea Eagles. Pages 111–116 In M. Ueta & M. J. Mcgrady (Eds.) First Symposium on Steller’s & White-Tailed Sea Eagles in East Asia. Wild Bird Society of Japan, Tokyo, Japan.
United Nations Environment Programme (2011) Literature Review: Effects of The Use of Lead Fishing Weights on Waterbirds & Wetlands. UNEP Agreement on The Conservation of African-Eurasian Migratory Waterbirds.
United States Endangered Species Act Of 1973 (ESA) (1973), As Amended, Pub. L. No. 93-205, 87 Stat. 884 (28 December 1973)
United States Fish & Wildlife Service (1973) Endangered Species Act. U.S.C. 1531-1544, 87 Stat. 884.
United States Fish & Wildlife Service (1976) Final Environmental Statement: Proposed Use of Steel Shot for Hunting Waterfowl in The United States. U.S. Department of Interior, Fish & Wildlife Service, Washington, DC, USA.
United States Fish & Wildlife Service (1976) Proposed Use of Steel Shot for Hunting Waterfowl in The United States, final Environmental Statement. Department of The Interior, US Fish & Wildlife Service, Washington, DC.
United States Fish & Wildlife Service (1986) Use of Lead Shot for Hunting Migratory Birds in The United States. Final Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement. U.S. Department of The Interior, Fish & Wildlife Service, Washington, DC, USA.
United States Fish & Wildlife Service (1988) Appendix 13: A Synopsis of The Nontoxic Shot Issue. In Final Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement: Issuance of Annual Regulations Permitting the Sport Hunting of Migratory Birds (SEISS 88) U.S. Department of The Interior, Fish & Wildlife Service, Washington, DC, USA. Pp. 317–319.
United States Fish & Wildlife Service (2016) Laws & Policies | Regulations & Policies | Interagency Policy Regarding the Role of State Agencies in ESA Activities.
United States Fish & Wildlife Service (2019a) Bald Eagle conservation. Accessed on 4 April 2019.
United States Fish & Wildlife Service (2019b) Bald Eagle breeding pairs 1990-2006. Accessed on 4 April 2019.
United States Geological Survey (2013) Mineral Industry Surveys: Lead in January 2013.
van Groenendael, J, de Kroon, H, & Caswell, H (1988) Projection matrices in population biology. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 3, 264-269.
Van Sickle, J, Attwell, C, & Craig, G (1987) Estimating population growth rate from an age distribution of natural deaths. Journal of Wildlife Management, 51, 941-948.
Vaughan, D, & Saila, S (1976) A method for determining mortality rates using the Leslie matrix. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 105, 380-383.
Veit, H, R Kendall, & P Scanlon (1982) The Effect of Lead Shot Ingestion on The Testes of Adult Ringed Turtle Doves (Strep– Tophelia Risoria) Avian Diseases 27:442–452.
Ventana Wildlife Society (2012) First-Year Results of a Free Nonlead Ammunition Program to Assist California Condor Recovery in Central California. Ventana Wildlife Society, Salinas, CA, USA.
Verbrugge L, Wenzel S, Berner J, Matz A (2009) Human Exposure to Lead from Ammunition in The Circumpolar North. In: Watson RT, Fuller M, Pokras M, Hunt WG, Eds. Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans. Boise, ID: The Peregrine Fund, 126-136. 19.
Vogel, H (2013) Effects of Lead Fishing Tackle on Loons In New Hampshire, 1989–2011.
Von Kuster, D, & D Schneberger (1992) Diet of The Great Horned Owl in Central Saskatchewan. Blue Jay 50: 195–200.
Vyas, N, J Spann, & G Heinz (2001) Lead Shot Toxicity to Passerines. Environmental Pollution 111:135–138.
Wald, A (1943) Tests of statistical hypothesis concerning several parameters when the
Walker, G (2007) Public Participation as Participatory Communication in Environmental Policy Decision-Making: From Concepts to Structured Conversations. Environmental Communication 1:99–110.
Walters, J, S Derrickson, D Fry, S Haig, J Marzluff, & J Wunderle, Jr (2010) Status of The California Condor & Efforts to Achieve Its Recovery. The Auk 127:969–1001.
Ward, E (2008) A review & comparison of four commonly used Bayesian & maximum likelihood model selection tools. Ecological Modelling, 211, 1-10.
Warner S, Britton E, Becker D, Coffey M (2014) Bald Eagle Lead Exposure in The Upper Midwest. Journal of Fish & Wildlife Management 5:208–216.
Waters, W (1898) – In: Jerome Cardano: a biographical study. Lawrence & Bullen, London, United Kingdom.
Watson, R, M Fuller, M Pokras, & W Hunt (Editors) (2009) Ingestion of Lead from Spent Ammunition: Implications for Wildlife & Humans. The Peregrine Fund, Boise, ID, USA.
Wayland M, Bollinger T (1999) Lead Exposure & Poisoning in Bald Eagles & Golden Eagles In The Canadian Prairie Provinces. Environ Pollut 104:341–350.
Wayland M, Wilson LK, Elliott JE, Miller MJR, Bollinger T, Mcadie M, Langelier K, Keating J, Froese JMW (2003) Mortality, Morbidity, & Lead Poisoning of Eagles in Western Canada, 1986–98. J Raptor Res 37:8–18.
Weisstein, E (2018) Beta-binomial distribution. From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. Accessed on 21 Sept. 2018.
Wendell, M, Sleeman J, Kratz G (2002) Retrospective Study of Morbidity & Mortality of Raptors Admitted to Colorado State University Veterinary Teaching Hospital During 1995 To 1998. J Wildl Dis 38:101–106.
Whittingham, M, P Stephens, R Bradbury, & R Freckleton (2006) Why do we still use stepwise modelling in ecology & behavior? Journal of Animal Ecology 75, 1182-1189.
Wiedenmann J, Fujiwara M, & Mangel M (2009) Transient population dynamics & viable stage or age distributions for effective conservation & recovery. Biological Conservation, 142, 2990-2996.
Wiemeyer, S, A Krynitsky, & S Wilbur (1983) Environmental Contaminants in Tissues, Foods, & Feces Of California Condors. Pages 4727–4739 In S. R. Wilbur & J. A. Jackson, (Eds.) Vulture Biology & Management. University of California Press, Los Angeles, California, USA.
Wiemeyer, S, R Jurek, & J Moore (1986) Environmental Contaminants in Surrogates, Foods, & Feathers of California Condors (Gymnogyps Californianus) Environmental Monitoring & Assessment 6:91–111.
Wiemeyer, S, J Scott, M Anderson, P Bloom, & C Stafford (1988) Environmental Contaminants in California Condors. Journal of Wildlife Management 52:238–247.
Wilbur, S (1978) The California Condor, 1966–1976: A Look at Its Past & Future. United States Department of The Interior, Fish & Wildlife Service. North American Fauna 72: 1–142.
Wilcove, D, & Murphy, D (1991) The Spotted Owl controversy & conservation biology. Conservation Biology, 5:3, 261-262.
Wilks, S (1938) The large-sample distribution of the likelihood ratio for testing composite hypotheses. Ann. Math. Statist. 9, 60-62.
Windingstad, R, S Kerr, L Locke, & J Hunt (1984) Lead Poisoning of S&– Hill Cranes (Grus Canadensis) Prairie Naturalist 16:21–24.
Wobester, G, & A Wobester (1992) Carcass Disappearance & Estimation of Mortality in a Simulated Die-Off of Small Birds. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 28:548–554.
Woiwod, I, & Hanski, I (1992) Patterns of density dependence in moths & aphids. Journal of Animal Ecology, 61, 619–629.
Wood, P (1992) Habitat use, movements, migration patterns, & survival rates of subadult Bald Eagles in north Florida. Ph.D. dissertation, Univ. of Florida, Gainesville, FL U.S.A.
Wootton, J, & Bell, D (1992) A metapopulation model of the peregrine falcon in California: viability & management strategies. Ecological Applications, 2, 307–321
Wyllie, I & Newton, I (1991) Demography of an increasing population of sparrowhawks. Journal of Animal Ecology, 60, 749-766.
Xu, C, & Gertner, G (2009) Uncertainty analysis of transient population dynamics. Ecological Modelling, 220, 283-293.
Yaw, T, Neumann, K, Bernard, L, Cancilla, J, Evans, T, Martin-Schwarze, A, & Zaffarano, B (2017) Lead poisoning in bald eagles admitted to wildlife rehabilitation facilities in Iowa, 2004-2014. Journal of Fish & Wildlife Management 8(2): 465-473.
Yearsley, J (2004) Transient population dynamics & short-term sensitivity analysis of matrix population models. Ecological Modelling, 177, 245-258.
Yoccoz, N (1991) Use, overuse, & misuse of significance tests in evolutionary biology & ecology. Bulletin of the Ecological Society of America, 72, 106–111.
Young, G (1968) A consideration of insecticide effects on hypothetical avian populations. Ecology, 49, 991-994.